A transcriptome study of the QseEF two-component system and the QseG membrane protein in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 : H7
- PMID: 20056703
- PMCID: PMC2889445
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.033027-0
A transcriptome study of the QseEF two-component system and the QseG membrane protein in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 : H7
Abstract
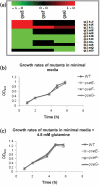
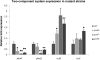
QseE is a sensor kinase that responds to epinephrine, sulfate and phosphate. QseE constitutes a two-component signalling system together with the QseF sigma(54)-dependent response regulator. Encoded within the same operon as qseEF is the qseG gene, which encodes a membrane protein involved in the translocation of a type III secretion effector protein of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) into epithelial cells. The qseEGF genes also form an operon with the glnB gene, which encodes the E. coli nitrogen sensor PII protein. Here we report a transcriptome analysis comparing qseE, qseF andqseG single mutants with the wild-type strain. This study revealed that the proteins encoded by these genes play a modest but significant role in iron uptake. Although QseEFG regulate genes involved in nitrogen utilization, these proteins do not play a notable role in nitrogen metabolism. In addition, QseEFG regulate transcription of the rcsBC and phoPQ two-component systems, linking several signal transduction pathways. The similarity of the microarray profiles of these mutants also indicates that these proteins work together. These data indicate that QseEFG are involved in the regulation of virulence and metabolism in EHEC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of lipoprotein QseG with sensor kinase QseE in the periplasm controls the phosphorylation state of the two-component system QseE/QseF in Escherichia coli.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 24;14(7):e1007547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007547. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30040820 Free PMC article.
-
The two-component system QseEF and the membrane protein QseG link adrenergic and stress sensing to bacterial pathogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Apr 7;106(14):5889-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811409106. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19289831 Free PMC article.
-
A novel two-component signaling system that activates transcription of an enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli effector involved in remodeling of host actin.J Bacteriol. 2007 Mar;189(6):2468-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.01848-06. Epub 2007 Jan 12. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17220220 Free PMC article.
-
The Epinephrine/Norepinephrine/Autoinducer-3 Interkingdom Signaling System in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;874:247-61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20215-0_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26589223 Review.
-
Quorum sensing and expression of virulence in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Int J Food Microbiol. 2003 Aug 15;85(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00482-8. Int J Food Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12810266 Review.
Cited by
-
Sigma factor N, liaison to an ntrC and rpoS dependent regulatory pathway controlling acid resistance and the LEE in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046288. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029465 Free PMC article.
-
Enteropathogens: Tuning Their Gene Expression for Hassle-Free Survival.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 9;9:3303. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03303. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30687282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between the QseC and QseE bacterial adrenergic sensor kinases in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2012 Dec;80(12):4344-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00803-12. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 23027532 Free PMC article.
-
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli virulence regulation by two bacterial adrenergic kinases, QseC and QseE.Infect Immun. 2012 Feb;80(2):688-703. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05921-11. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22144490 Free PMC article.
-
What a Dinner Party! Mechanisms and Functions of Interkingdom Signaling in Host-Pathogen Associations.mBio. 2016 Mar 1;7(2):e01748. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01748-15. mBio. 2016. PMID: 26933054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anonymous (1997). Applied Biosystems Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System: User Bulletin #2. Norwalk, CT: Perkin-Elmer Corp.
-
- Bader, M. W., Sanowar, S., Daley, M. E., Schneider, A. R., Cho, U., Xu, W., Klevit, R. E., Le Moual, H. & Miller, S. I. (2005). Recognition of antimicrobial peptides by a bacterial sensor kinase. Cell 122, 461–472. - PubMed
-
- Bolstad, B. M., Irizarry, R. A., Astrand, M. & Speed, T. P. (2003). A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19, 185–193. - PubMed
-
- Campellone, K. G., Robbins, D. & Leong, J. M. (2004). EspFU is a translocated EHEC effector that interacts with Tir and N-WASP and promotes Nck-independent actin assembly. Dev Cell 7, 217–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

