MicroRNA-204/211 alters epithelial physiology
- PMID: 20056717
- PMCID: PMC3231816
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.08-125856
MicroRNA-204/211 alters epithelial physiology
Abstract
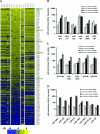
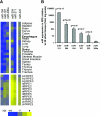
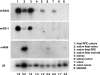
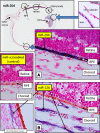
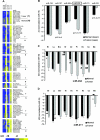
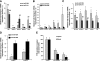
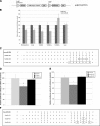
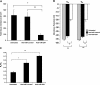
MicroRNA (miRNA) expression in fetal human retinal pigment epithelium (hfRPE), retina, and choroid were pairwise compared to determine those miRNAs that are enriched by 10-fold or more in each tissue compared with both of its neighbors. miRs-184, 187, 200a/200b, 204/211, and 221/222 are enriched in hfRPE by 10- to 754-fold compared with neuroretina or choroid (P<0.05). Five of these miRNAs are enriched in RPE compared with 20 tissues throughout the body and are 10- to 20,000-fold more highly expressed (P<0.005). miR-204 and 211 are the most highly expressed in the RPE. In addition, expression of miR-204/211 is significantly lower in the NCI60 tumor cell line panel compared with that in 13 normal tissues, suggesting the progressive disruption of epithelial barriers and increased proliferation. We demonstrated that TGF-beta receptor 2 (TGF-betaR2) and SNAIL2 are direct targets of miR-204 and that a reduction in miR-204 expression leads to reduced expression of claudins 10, 16, and 19 (message/protein) consistent with our observation that anti-miR-204/211 decreased transepithelial resistance by 80% and reduced cell membrane voltage and conductance. The anti-miR-204-induced decrease in Kir7.1 protein levels suggests a signaling pathway that connects TGF-betaR2 and maintenance of potassium homeostasis. Overall, these data indicate a critical role for miR-204/211 in maintaining epithelial barrier function and cell physiology.
Figures
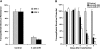


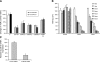
References
-
- Shin K., Fogg V. C., Margolis B. Tight junctions and cell polarity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:207–235. - PubMed
-
- Van Itallie C. M., Anderson J. M. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:403–429. - PubMed
-
- Fisher S. K., Steinberg R. H. Origin and organization of pigment epithelial apical projections to cones in cat retina. J Comp Neurol. 1982;206:131–145. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

