Rapid development of hypertension and proteinuria with cediranib, an oral vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor
- PMID: 20056761
- PMCID: PMC2827577
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08111109
Rapid development of hypertension and proteinuria with cediranib, an oral vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hypertension and proteinuria are common but poorly understood renal toxicities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor signaling pathway inhibitors. In this phase II study of cediranib (AZD2171) for recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer, the time course and severity of BP changes and proteinuria were characterized.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: 46 women ages 41 to 77 years were treated with cediranib. 26% had baseline hypertension. Twice-daily BP was recorded. Urinalyses were performed every 2 weeks, and in some patients proteinuria was further quantified.
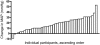
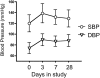
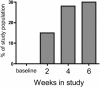
Results: 31 women (67%) developed hypertension by day 3; 87% by the end of the study. 43% developed grade > or =3 hypertension. Mean systolic BP increase over 3 days was 18 mmHg. Women above the mean age (> or =57 years) had a larger rise in systolic BP by day 3 (15.9 versus 7.0 mmHg). 14 women developed proteinuria. There was a dose response (45 versus 30 mg daily). Proteinuria also developed rapidly, with 7 of 14 women developing proteinuria within 2 weeks. Only 7 of 20 women who developed grade 3 hypertension developed proteinuria.
Conclusions: Cediranib induced a rapid but variable rise in BP within 3 days of initiation in most patients. Proteinuria was common and also developed rapidly. The rapid development of hypertension suggests that acute inhibition of VEGF-dependent vasodilation might explain the BP rise with VEGF inhibitors. Clinicians must be vigilant in early detection and management of toxicities of this expanding drug class, especially in older patients.
Figures
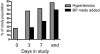
References
-
- Wedge SR, Kendrew J, Hennequin LF, Valentine PJ, Barry ST, Brave SR, Smith NR, James NH, Dukes M, Curwen JO, Chester R, Jackson JA, Boffey SJ, Kilburn LL, Barnett S, Richmond GH, Wadsworth PF, Walker M, Bigley AL, Taylor ST, Cooper L, Beck S, Jurgensmeier JM, Ogilvie DJ: AZD2171: A highly potent, orally bioavailable, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res 65: 4389–4400, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Laurie SA, Gauthier I, Arnold A, Shepherd FA, Ellis PM, Chen E, Goss G, Powers J, Walsh W, Tu D, Robertson J, Puchalski TA, Seymour L: Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of daily oral AZD2171, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor tyrosine kinases, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the National Cancer Institute of Canada clinical trials group. J Clin Oncol 26: 1871–1878, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto N, Tamura T, Yamada K, Yamada Y, Nokihara H, Fujiwara Y, Takahashi T, Murakami H, Boku N, Yamazaki K, Puchalski TA, Shin E: Phase I, dose escalation and pharmacokinetic study of cediranib (RECENTIN), a highly potent and selective VEGFR signaling inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64: 1165–1172, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Izzedine H, Rixe O, Billemont B, Baumelou A, Deray G: Angiogenesis inhibitor therapies: Focus on kidney toxicity and hypertension. Am J Kidney Dis 50: 203–218, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

