Pulmonary infection with an interferon-gamma-producing Cryptococcus neoformans strain results in classical macrophage activation and protection
- PMID: 20056835
- PMCID: PMC2808084
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090634
Pulmonary infection with an interferon-gamma-producing Cryptococcus neoformans strain results in classical macrophage activation and protection
Abstract
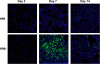
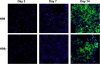
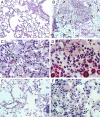
Alternative macrophage activation is associated with exacerbated disease in murine models of pulmonary cryptococcosis. The present study evaluated the efficacy of interferon-gamma transgene expression by Cryptococcus neoformans strain H99gamma in abrogating alternative macrophage activation in infected mice. Macrophage recruitment into the lungs of mice after infection with C. neoformans strain H99gamma was comparable with that observed in mice challenged with wild-type C. neoformans. However, pulmonary infection in mice with C. neoformans strain H99gamma was associated with reduced pulmonary fungal burden, increased pulmonary Th1-type and interleukin-17 cytokine production, and classical macrophage activation as evidenced by increased inducible nitric oxide synthase expression, histological evidence of enhanced macrophage fungicidal activity, and resolution of inflammation. In contrast, progressive pulmonary infection, enhanced Th2-type cytokine production, and the induction of alternatively activated macrophages expressing arginase-1, found in inflammatory zone 1, Ym1, and macrophage mannose receptor were observed in the lungs of mice infected with wild-type C. neoformans. These alternatively activated macrophages were also shown to harbor highly encapsulated, replicating cryptococci. Our results demonstrate that pulmonary infection with C. neoformans strain H99gamma results in the induction of classically activated macrophages and promotes fungal clearance. These studies indicate that phenotype, as opposed to quantity, of infiltrating macrophages correlates with protection against pulmonary C. neoformans infection.
Figures







References
-
- Powderly WG. Cryptococcal meningitis and AIDS. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:837–842. - PubMed
-
- Arora S, Hernandez Y, Erb-Downward JR, McDonald RA, Toews GB, Huffnagle GB. Role of IFN-γ in regulating T2 immunity and the development of alternatively activated macrophages during allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis. J Immunol. 2005;174:6346–6356. - PubMed
-
- Collins HL, Bancroft GJ. Cytokine enhancement of complement-dependent phagocytosis by macrophages: synergy of tumor necrosis factor-α and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eur J Immunol. 1992;22:1447–1454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

