Essential role of the histone methyltransferase G9a in cocaine-induced plasticity
- PMID: 20056891
- PMCID: PMC2820240
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1179438
Essential role of the histone methyltransferase G9a in cocaine-induced plasticity
Abstract
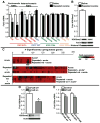
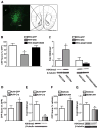
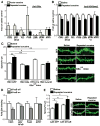
Cocaine-induced alterations in gene expression cause changes in neuronal morphology and behavior that may underlie cocaine addiction. In mice, we identified an essential role for histone 3 lysine 9 (H3K9) dimethylation and the lysine dimethyltransferase G9a in cocaine-induced structural and behavioral plasticity. Repeated cocaine administration reduced global levels of H3K9 dimethylation in the nucleus accumbens. This reduction in histone methylation was mediated through the repression of G9a in this brain region, which was regulated by the cocaine-induced transcription factor DeltaFosB. Using conditional mutagenesis and viral-mediated gene transfer, we found that G9a down-regulation increased the dendritic spine plasticity of nucleus accumbens neurons and enhanced the preference for cocaine, thereby establishing a crucial role for histone methylation in the long-term actions of cocaine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of the Histone Dimethyltransferase G9a in Nucleus Accumbens Shell Increases Cocaine Self-Administration, Stress-Induced Reinstatement, and Anxiety.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 24;38(4):803-813. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1657-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29217682 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing role for Egr3 in nucleus accumbens cell subtypes in cocaine action.J Neurosci. 2015 May 20;35(20):7927-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0548-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25995477 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of the histone di-methyltransferase G9a in nucleus accumbens shell decreases cocaine self-administration, stress-induced reinstatement, and anxiety.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jul;44(8):1370-1376. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0305-4. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30587852 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H3K9 methyltransferase G9a and the related molecule GLP.Genes Dev. 2011 Apr 15;25(8):781-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.2027411. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21498567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phenethylisothiocyanate alters site- and promoter-specific histone tail modifications in cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e64535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064535. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724058 Free PMC article.
-
Incubation of methamphetamine craving is associated with selective increases in expression of Bdnf and trkb, glutamate receptors, and epigenetic enzymes in cue-activated fos-expressing dorsal striatal neurons.J Neurosci. 2015 May 27;35(21):8232-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1022-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26019338 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal Programming by Methyl Donors Modulates Central Inflammation and Prevents Food Addiction-Like Behavior in Rats.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 3;14:452. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00452. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32581665 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and structural responses to chronic cocaine require a feedforward loop involving ΔFosB and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the nucleus accumbens shell.J Neurosci. 2013 Mar 6;33(10):4295-307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5192-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23467346 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone acetylation in cocaine-induced neural plasticity and behavior.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jan;38(1):94-110. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.154. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22910457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

