Green tea catechin EGCG inhibits ileal apical sodium bile acid transporter ASBT
- PMID: 20056894
- PMCID: PMC2838517
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00360.2009
Green tea catechin EGCG inhibits ileal apical sodium bile acid transporter ASBT
Abstract
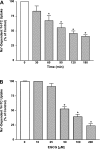
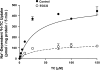
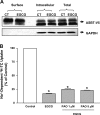
Green tea catechins exhibit hypocholesterolemic effects probably via their inhibitory effects on intestinal bile acid absorption. Ileal apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) is responsible for reabsorption of bile acids. The present studies were, therefore, designed to investigate the modulation of ASBT function and membrane expression by green tea catechins in human embryonic kidney HEK-293 cells stably transfected with ASBT-V5 fusion protein and intestinal Caco-2 monolayers. Our data showed that ASBT activity was significantly decreased by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) but not other green tea catechins. Inhibition of PKC, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and MAPK-dependent pathways failed to block the reduction in ASBT activity by EGCG. Kinetics studies showed a significant decrease in the V(max) of the transporter, whereas total ASBT content on the plasma membrane was unaltered by EGCG. Concomitant with the decrease in ASBT function, EGCG significantly reduced ASBT pool in the detergent-insoluble fraction, while increasing its presence in the detergent-soluble fraction of plasma membrane. Furthermore, EGCG decreased the association of ASBT with floating lipid raft fractions of cellular membrane on Optiprep density gradient. In conclusion, our data demonstrate a novel role of lipid rafts in the modulation of ASBT function by the dietary component EGCG, which may underlie the hypocholesterolemic effects of green tea.
Figures

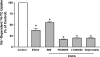



References
-
- Adachi S, Nagao T, Ingolfsson HI, Maxfield FR, Andersen OS, Kopelovich L, Weinstein IB. The inhibitory effect of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor is associated with altered lipid order in HT29 colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 67: 6493–6501, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Albrecht DS, Clubbs EA, Ferruzzi M, Bomser JA. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits PC-3 prostate cancer cell proliferation via MEK-independent ERK1/2 activation. Chem Biol Interact 171: 89–95, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Alpini G, Glaser S, Baiocchi L, Francis H, Xia X, Lesage G. Secretin activation of the apical Na+-dependent bile acid transporter is associated with cholehepatic shunting in rats. Hepatology 41: 1037–1045, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Alrefai WA, Gill RK. Bile acid transporters: structure, function, regulation and pathophysiological implications. Pharm Res 24: 1803–1823, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Alrefai WA, Sarwar Z, Tyagi S, Saksena S, Dudeja PK, Gill RK. Cholesterol modulates human intestinal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288: G978–G985, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

