Novel thioredoxin-related transmembrane protein TMX4 has reductase activity
- PMID: 20056998
- PMCID: PMC2844163
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082545
Novel thioredoxin-related transmembrane protein TMX4 has reductase activity
Abstract
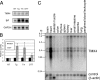
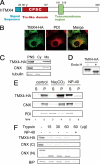
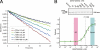
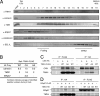
In the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a number of thioredoxin (Trx) superfamily proteins are present to enable correct disulfide bond formation of secretory and membrane proteins via Trx-like domains. Here, we identified a novel transmembrane Trx-like protein 4 (TMX4), in the ER of mammalian cells. TMX4, a type I transmembrane protein, was localized to the ER and possessed a Trx-like domain that faced the ER lumen. A maleimide alkylation assay showed that a catalytic CXXC motif in the TMX4 Trx-like domain underwent changes in its redox state depending on cellular redox conditions, and, in the normal state, most of the endogenous TMX4 existed in the oxidized form. Using a purified recombinant protein containing the Trx-like domain of TMX4 (TMX4-Trx), we confirmed that this domain had reductase activity in vitro. The redox potential of this domain (-171.5 mV; 30 degrees C at pH 7.0) indicated that TMX4 could work as a reductase in the environment of the ER. TMX4 had no effect on the acceleration of ER-associated degradation. Because TMX4 interacted with calnexin and ERp57 by co-immunoprecipitation assay, the role of TMX4 may be to enable protein folding in cooperation with these proteins consisting of folding complex in the ER.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A di-arginine motif contributes to the ER localization of the type I transmembrane ER oxidoreductase TMX4.Biochem J. 2009 Dec 14;425(1):195-205. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091064. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19811453
-
Identification of the Primary Factors Determining theSpecificity of Human VKORC1 Recognition by Thioredoxin-Fold Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 14;22(2):802. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020802. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33466919 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein 57 (ERp57) oxidatively inactivates human transglutaminase 2.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 23;293(8):2640-2649. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001382. Epub 2018 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29305423 Free PMC article.
-
The thioredoxin superfamily in oxidative protein folding.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jul 20;21(3):457-70. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.5849. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24483600 Review.
-
Methods to identify the substrates of thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases.Protein Sci. 2019 Jan;28(1):30-40. doi: 10.1002/pro.3530. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 30341785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin-related transmembrane protein 2 (TMX2) regulates the Ran protein gradient and importin-β-dependent nuclear cargo transport.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 25;9(1):15296. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51773-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31653923 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of new transmembrane proteins concentrated at the nuclear envelope using organellar proteomics of mesenchymal cells.Nucleus. 2019 Dec;10(1):126-143. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2019.1618175. Nucleus. 2019. PMID: 31142202 Free PMC article.
-
TMX5/TXNDC15, a natural trapping mutant of the PDI family is a client of the proteostatic factor ERp44.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Sep 30;7(12):e202403047. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403047. Print 2024 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39348940 Free PMC article.
-
The human protein disulfide isomerase gene family.Hum Genomics. 2012 Jul 5;6(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-6-6. Hum Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23245351 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Determinants of TMC Protein Biogenesis and Trafficking.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 1;26(13):6356. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136356. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sevier C. S., Kaiser C. A. (2002) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 836–847 - PubMed
-
- Hwang C., Sinskey A. J., Lodish H. F. (1992) Science 257, 1496–1502 - PubMed
-
- Sevier C. S., Kaiser C. A. (2006) Antioxid. Redox Signal. 8, 797–811 - PubMed
-
- Hebert D. N., Molinari M. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 1377–1408 - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C., Ellgaard L. (2008) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1783, 535–548 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

