Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the MIF4G domain of DAP5
- PMID: 20057060
- PMCID: PMC2805526
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109044315
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the MIF4G domain of DAP5
Abstract
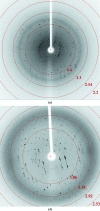
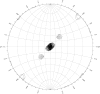
Death-associated protein 5 (DAP5) is a member of the eIF4G family of scaffolding proteins that mediate cap-independent translation initiation by recruiting the translational machinery to internal ribosomal entry sites (IRESs) on mRNA. The MIF4G domain of DAP5 directly interacts with the eukaryotic initiation factors eIF4A and eIF3 and enhances the translation of several viral and cellular IRESs. Here, the crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the MIF4G domain of DAP5 is presented.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural analysis of the DAP5 MIF4G domain and its interaction with eIF4A.Structure. 2013 Apr 2;21(4):517-27. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23478064 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the MIF4G domain of the Trypanosoma cruzi translation initiation factor EIF4G5.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019 Dec 1;75(Pt 12):738-743. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X19015061. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31797815 Free PMC article.
-
A novel form of DAP5 protein accumulates in apoptotic cells as a result of caspase cleavage and internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;20(2):496-506. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.2.496-506.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10611228 Free PMC article.
-
The translation initiation factor DAP5 is a regulator of cell survival during mitosis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Jan 15;8(2):204-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.2.7384. Epub 2009 Jan 10. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19158497 Review.
-
[Translational control by the poly(A) binding protein: a check for mRNA integrity].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Jul-Aug;40(4):684-93. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 16913227 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
A newly identified Leishmania IF4E-interacting protein, Leish4E-IP2, modulates the activity of cap-binding protein paralogs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 May 7;48(8):4405-4417. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa173. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32232353 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of DAP5 by coxsackievirus B3 2A protease facilitates viral replication and enhances apoptosis by altering translation of IRES-containing genes.Cell Death Differ. 2016 May;23(5):828-40. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.145. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26586572 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of the DAP5 MIF4G domain and its interaction with eIF4A.Structure. 2013 Apr 2;21(4):517-27. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23478064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brünger, A. T., Adams, P. D., Clore, G. M., DeLano, W. L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Jiang, J.-S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N. S., Read, R. J., Rice, L. M., Simonson, T. & Warren, G. L. (1998). Acta Cryst. D54, 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Cowtan, K. D. & Main, P. (1993). Acta Cryst. D49, 148–157. - PubMed
-
- Derry, M. C., Yanagiya, A., Martineau, Y. & Sonenberg, N. (2006). Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol.71, 537–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

