Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data analysis of stenodactylin, a highly toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein from Adenia stenodactyla
- PMID: 20057070
- PMCID: PMC2805536
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109047654
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data analysis of stenodactylin, a highly toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein from Adenia stenodactyla
Abstract
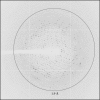
Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) inhibit protein synthesis and induce cell death by removing a single adenine from a specific rRNA loop. They can be divided into two main groups: type 1 and type 2 RIPs. Type 1 RIPs are single-chain enzymes with N-glycosidase activity. Type 2 RIPs contain two chains (A and B) linked by a disulfide bond. The A chain has RIP enzymatic activity, whereas the B chain shows lectin activity and is able to bind to glycosylated receptors on the cell surface. Stenodactylin is a type 2 RIP from the caudex of Adenia stenodactyla from the Passifloraceae family that has been recently purified and characterized. It shows a strong enzymatic activity towards several substrates and is more cytotoxic than other toxins of the same type. Here, the crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data analysis of stenodactylin are reported. This RIP forms crystals that diffract to high resolution (up to 2.15 A). The best data set was obtained by merging data collected from two crystals. Stenodactylin crystals belonged to the centred monoclinic space group C2 and contained two molecules in the asymmetric unit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of highly toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Adenia lanceolata and Adenia stenodactyla (Passifloraceae).Toxicon. 2007 Jul;50(1):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.02.020. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17434551
-
Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 22;13(2):81. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020081. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33499082 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and intracellular routing of the plant-toxic lectins, lanceolin and stenodactylin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1800(12):1276-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.09.006. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20933061
-
Description, distribution, activity and phylogenetic relationship of ribosome-inactivating proteins in plants, fungi and bacteria.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004 Jun;4(5):461-76. doi: 10.2174/1389557043403891. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15180503 Review.
-
Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: more than RNA N-glycosidases?FASEB J. 2001 Jul;15(9):1493-506. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0751rev. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11427481 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Response to the Plant Toxin Stenodactylin in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Involves Inflammatory and Apoptotic Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 8;11:630. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00630. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32457623 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicity studies of the genus Adenia.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 21;16:1581659. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1581659. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40469989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary Sequence and 3D Structure Prediction of the Plant Toxin Stenodactylin.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 21;12(9):538. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090538. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Audi, J., Belson, M., Patel, M., Schier, J. & Osterloh, J. (2005). JAMA, 294, 2342–2351. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri, L., Valbonesi, P., Bondioli, M., Lugo Alvarez, M., Dal Monte, P., Landini, M. P. & Stirpe, F. (2001). FEBS Lett.505, 196–197. - PubMed
-
- Bigalke, H. & Rummel, A. (2005). Toxicology, 214, 210–220. - PubMed
-
- Bolognesi, A. & Polito, L. (2004). Mini Rev. Med. Chem.4, 563–583. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous