Early cardiovascular abnormalities in newly diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 20057899
- PMCID: PMC2801630
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s8300
Early cardiovascular abnormalities in newly diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
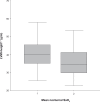
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with high cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Recent studies have shown that it is associated with atherosclerosis and left ventricular dysfunction markers. The aim of this study was to assess the cardiovascular effects of OSA depending on its severity, in patients without clinically diagnosed cardiovascular disease. One hundred thirty newly diagnosed, nondiabetic OSA patients (mean age 49 +/- 10 years), without vasoactive treatment were included. They underwent clinical and ambulatory blood pressure measurements, echocardiography, carotid ultrasound examination, and a carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) measurement. Seventy-five percent of the subjects were hypertensive according to the clinical or ambulatory measurement. More patients with the most severe forms (respiratory disturbance index >37/hour) had a nondipper profile (52% vs 34%; P = 0.025) and their left ventricular mass was higher (40 +/- 7 vs 36 +/- 8 g/m, p = 0.014). This last parameter was independently and inversely associated with mean nocturnal oxygen saturation (P = 0.004). PWV and carotid intima-media thickness did not differ between one OSA severity group to another, but the prevalence of carotid hypertrophy was higher when mean SaO(2) was below 93.5% (29.5 vs 16%; P = 0.05). Our study shows that in OSA patients without clinically diagnosed cardiovascular disease, there is a significant left ventricular and arterial effect, which is even more marked when OSA is severe.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00764218.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; hypertension; intima-media thickness; left ventricular hypertrophy; obstructive sleep apnea.
Figures

References
-
- Kapur V, Strohl KP, Redline S, Iber C, O’Connor G, Nieto J. Underdiagnosis of sleep apnea syndrome in U.S. communities. Sleep Breath. 2002;6:49–54. - PubMed
-
- Miller WP. Cardiac arrhythmias and conduction disturbances in the sleep apnea syndrome. Prevalence and significance. Am J Med. 1982;73:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Peppard P, Palta M, et al. Population-based study of sleep-disordered breathing as a risk factor for hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:1746–1752. - PubMed
-
- Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, et al. Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep Heart Health Study. JAMA. 2000;283:1829–1836. - PubMed
-
- Mooe T, Franklin KA, Holmström K, Rabben T, Wiklund U. Sleep-disordered breathing and coronary artery disease: long-term prognosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1910–1913. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

