Intranasal delivery of influenza subunit vaccine formulated with GEM particles as an adjuvant
- PMID: 20058113
- PMCID: PMC2844513
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-009-9168-2
Intranasal delivery of influenza subunit vaccine formulated with GEM particles as an adjuvant
Abstract
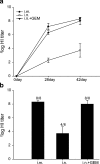
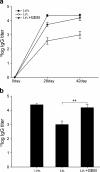
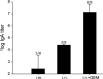
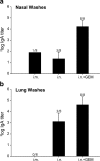
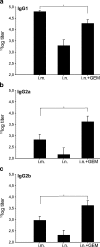
Nasal administration of influenza vaccine has the potential to facilitate influenza control and prevention. However, when administered intranasally (i.n.), commercially available inactivated vaccines only generate systemic and mucosal immune responses if strong adjuvants are used, which are often associated with safety problems. We describe the successful use of a safe adjuvant Gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles derived from the food-grade bacterium Lactococcus lactis for i.n. vaccination with subunit influenza vaccine in mice. It is shown that simple admixing of the vaccine with the GEM particles results in a strongly enhanced immune response. Already after one booster, the i.n. delivered GEM subunit vaccine resulted in hemagglutination inhibition titers in serum at a level equal to the conventional intramuscular (i.m.) route. Moreover, i.n. immunization with GEM subunit vaccine elicited superior mucosal and Th1 skewed immune responses compared to those induced by i.m. and i.n. administered subunit vaccine alone. In conclusion, GEM particles act as a potent adjuvant for i.n. influenza immunization.
Figures

References
-
- WHO, influenza, fact sheet 211, revised 2003.
-
- Couch RB, Kasel JA, Glezen WP, Cate TR, Six HR, Taber LH, et al. Influenza: its control in persons and populations. J Infect Dis. 1986;153(3):431–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

