In situ hybridization of neuropeptide-encoding transcripts afp-1, afp-3, and afp-4 in neurons of the nematode Ascaris suum
- PMID: 20058230
- PMCID: PMC2972677
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22251
In situ hybridization of neuropeptide-encoding transcripts afp-1, afp-3, and afp-4 in neurons of the nematode Ascaris suum
Abstract
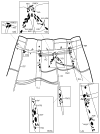
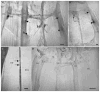
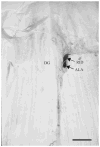
The gene transcripts encoding both the AF8 and AF2 neuropeptides of the nematode Ascaris suum have been identified, cloned, and sequenced. The AF8 transcript (afp-3) encodes five identical copies of AF8; each peptide-encoding region is flanked by the appropriate dibasic or monobasic cleavage processing sites. The AF2 transcript (afp-4) encodes three identical copies of AF2 along with the appropriate cleavage sites. In contrast, the afp-1 transcript (Edison et al. [1997] Peptides 18:929-935) encodes six different AF peptides (AF3, 4, 10, 13, 14, 20) which all share a -PGVLRFamide C-terminus but have different N-terminal sequences. By using in situ hybridization, gene transcript expression patterns of afp-1, afp-3, and afp-4 (As-flp-18, As-flp-6, and As-flp-14, respectively, in the naming convention proposed by Blaxter et al. [1997] Parasitol Today 13:416-417) were determined in the adult A. suum anterior nervous system. Each gene transcript can be localized to a different subset of neurons. These subsets of neurons are different from the subsets of Caenorhabditis elegans neurons that were shown to express identical or similar peptides by the use of promoter GFP constructs (Kim and Li [2004] J Comp Neurol 475:540-550).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Different neuropeptides are expressed in different functional subsets of cholinergic excitatory motorneurons in the nematode Ascaris suum.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jun 17;6(6):855-70. doi: 10.1021/cn5003623. Epub 2015 Apr 9. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25812635 Free PMC article.
-
Three independent techniques localize expression of transcript afp-11 and its bioactive peptide products to the paired AVK neurons in Ascaris suum: in situ hybridization, immunocytochemistry, and single cell mass spectrometry.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Mar 20;4(3):418-34. doi: 10.1021/cn3001334. Epub 2012 Dec 27. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23509978 Free PMC article.
-
afp-1: a gene encoding multiple transcripts of a new class of FMRFamide-like neuropeptides in the nematode Ascaris suum.Peptides. 1997;18(7):929-35. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(97)00047-8. Peptides. 1997. PMID: 9357048
-
Neuropeptide gene families in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;897:239-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07895.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10676452 Review.
-
The ever-expanding neuropeptide gene families in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Parasitology. 2005;131 Suppl:S109-27. doi: 10.1017/S0031182005009376. Parasitology. 2005. PMID: 16569285 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping neuropeptide expression by mass spectrometry in single dissected identified neurons from the dorsal ganglion of the nematode Ascaris suum.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2010 Jul 21;1(7):505-519. doi: 10.1021/cn1000217. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20806053 Free PMC article.
-
Different neuropeptides are expressed in different functional subsets of cholinergic excitatory motorneurons in the nematode Ascaris suum.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jun 17;6(6):855-70. doi: 10.1021/cn5003623. Epub 2015 Apr 9. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25812635 Free PMC article.
-
A specific antibody to neuropeptide AF1 (KNEFIRFamide) recognizes a small subset of neurons in Ascaris suum: differences from Caenorhabditis elegans.J Comp Neurol. 2011 Jun 1;519(8):1546-61. doi: 10.1002/cne.22584. J Comp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21452223 Free PMC article.
-
Parasite neuropeptide biology: Seeding rational drug target selection?Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2011 Nov 15;2:76-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2011.10.004. eCollection 2012 Dec. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2011. PMID: 24533265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The FMRFamide-Like Peptide Family in Nematodes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Jun 16;5:90. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00090. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24982652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Angstadt JD, Donmoyer JE, Stretton AOW. Retrovesicular ganglion of the nematode Ascaris. J Comp Neurol. 1989;284:374–388. - PubMed
-
- Blaxter ML, Guiliano DB, Scott AL, Williams SA. A unified nomenclature for filarial genes. Parasitol Today. 1997;13:416–417. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal T. The C. elegans Research Community . Wormbook. 2005. Trans-splicing and operons. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury AF, Smyth DG. Biosynthesis of the C-terminal amide in peptide hormones. Biosci Rep. 1987;7:907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

