The 19S proteasomal lid subunit POH1 enhances the transcriptional activation by Mitf in osteoclasts
- PMID: 20058232
- PMCID: PMC3273965
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22475
The 19S proteasomal lid subunit POH1 enhances the transcriptional activation by Mitf in osteoclasts
Abstract
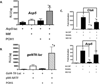
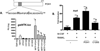
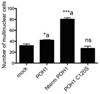
The microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (Mitf) regulates gene expression required for osteoclast differentiation. Genes regulated by Mitf have been previously identified. However, proteins that interact and regulate Mitf's activity in osteoclasts are not well known. Here, we report that POH1, a subunit of the 19S proteasome lid is a regulator of Mitf. We show that POH1 and Mitf interact in osteoclasts and that this interaction is dependent on RANKL signaling. Overexpression of POH1 increased Mitf's activation of 5XGal4-TK and Acp5 promoters. The amino terminus of POH1 mediates the binding to Mitf and is sufficient to increase Mitf's transcriptional activity. Finally, we show that mutations in the JAMM motif of POH1 reduced Mitf activation of promoters. In summary, our results identify a novel mechanism of Mitf regulation in osteoclasts by POH1.
Copyright 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
C-TAK1 interacts with microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, Mitf, but not the related family member Tfe3.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Apr 16;394(4):890-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.034. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20214879 Free PMC article.
-
Defective co-activator recruitment in osteoclasts from microphthalmia-oak ridge mutant mice.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jul;220(1):230-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21755. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19288495 Free PMC article.
-
Eos, MITF, and PU.1 recruit corepressors to osteoclast-specific genes in committed myeloid progenitors.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;27(11):4018-27. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01839-06. Epub 2007 Apr 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17403896 Free PMC article.
-
Mitf and Tfe3: members of a b-HLH-ZIP transcription factor family essential for osteoclast development and function.Bone. 2004 Apr;34(4):689-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2003.08.014. Bone. 2004. PMID: 15050900 Review.
-
MITF-the first 25 years.Genes Dev. 2019 Aug 1;33(15-16):983-1007. doi: 10.1101/gad.324657.119. Epub 2019 May 23. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 31123060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PSMD14 is a novel prognostic marker and therapeutic target in osteosarcoma.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Jun 11;19(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01489-y. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38863002 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinating Enzymes and Bone Remodeling.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jul 8;2018:3712083. doi: 10.1155/2018/3712083. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30123285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The deubiquitinating enzyme PSMD14 facilitates tumor growth and chemoresistance through stabilizing the ALK2 receptor in the initiation of BMP6 signaling pathway.EBioMedicine. 2019 Nov;49:55-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.039. Epub 2019 Nov 1. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31685442 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Basis of JAMM Deubiquitinating Enzymes in Disease.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 29;12(7):910. doi: 10.3390/biom12070910. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia Promotes Osteoclast Differentiation by Weakening USP18-Mediated Suppression on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):10. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010010. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin proteolytic system and pathogenesis of human diseases: a novel platform for mechanism-based drug targeting. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:474–481. - PubMed
-
- Glickman MH, Rubin DM, Coux O, Wefes I, Pfeifer G, Cjeka Z, Baumeister W, Fried VA, Finley D. A subcomplex of the proteasome regulatory particle required for ubiquitin-conjugate degradation and related to the COP9-signalosome and eIF3. Cell. 1998;94:615–623. - PubMed
-
- Glickman MH, Rubin DM, Fu H, Larsen CN, Coux O, Wefes I, Pfeifer G, Cjeka Z, Vierstra R, Baumeister W, Fried V, Finley D. Functional analysis of the proteasome regulatory particle. Mol Biol Rep. 1999;26:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Guterman A, Glickman MH. Deubiquitinating enzymes are IN/(trinsic to proteasome function) Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2004;5:201–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

