Localization of a GABA transporter to glial cells in the developing and adult olfactory pathway of the moth Manduca sexta
- PMID: 20058309
- PMCID: PMC2920212
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22244
Localization of a GABA transporter to glial cells in the developing and adult olfactory pathway of the moth Manduca sexta
Abstract
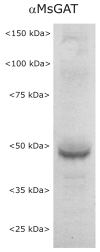
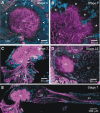
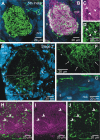
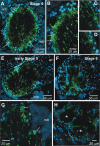
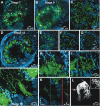
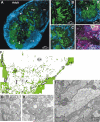
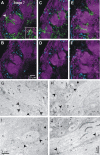
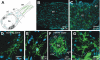
Glial cells have several critical roles in the developing and adult olfactory (antennal) lobe of the moth Manduca sexta. Early in development, glial cells occupy discrete regions of the developing olfactory pathway and processes of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic neurons extend into some of these regions. Because GABA is known to have developmental effects in a variety of systems, we explored the possibility that the glial cells express a GABA transporter that could regulate GABA levels to which olfactory neurons and glial cells are exposed. By using an antibody raised against a characterized high-affinity M. sexta GABA transporter with high sequence homology to known mammalian GABA transporters (Mbungu et al. [1995] Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 318:489-497; Umesh and Gill [2002] J. Comp. Neurol. 448:388-398), we found that the GABA transporter is localized to subsets of centrally derived glial cells during metamorphic adult development. The transporter persists into adulthood in a subset of the neuropil-associated glial cells, but its distribution pattern as determined by light-and electron-microscopic-level immunocytochemistry indicates that it could not serve to regulate GABA concentration in the synaptic cleft. Instead, its role is more likely to regulate extracellular GABA levels within the glomerular neuropil. Expression in the sorting zone glial cells disappears after the period of olfactory receptor axon ingrowth, but may be important during ingrowth if GABA regulates axon growth. Glial cells take up GABA, and that uptake can be blocked by L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid (DABA). This is the first molecular evidence that the central glial cell population in this pathway is heterogeneous.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunolocalization of synaptotagmin for the study of synapses in the developing antennal lobe of Manduca sexta.J Comp Neurol. 2001 Dec 24;441(4):277-87. doi: 10.1002/cne.1412. J Comp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11745650
-
Glial cells stabilize axonal protoglomeruli in the developing olfactory lobe of the moth Manduca sexta.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Sep 9;373(1):118-28. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960909)373:1<118::AID-CNE10>3.0.CO;2-G. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8876467
-
Olfactory receptor axons influence the development of glial potassium currents in the antennal lobe of the moth Manduca sexta.Glia. 2001 Dec;36(3):309-20. doi: 10.1002/glia.1118. Glia. 2001. PMID: 11746768
-
Calcium signaling in invertebrate glial cells.Glia. 2006 Nov 15;54(7):642-649. doi: 10.1002/glia.20368. Glia. 2006. PMID: 17006892 Review.
-
The roles of local interneurons in the processing of olfactory information in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta.Acta Biol Hung. 1992;43(1-4):167-74. Acta Biol Hung. 1992. PMID: 1299109 Review.
Cited by
-
Origin and development of neuropil glia of the Drosophila larval and adult brain: Two distinct glial populations derived from separate progenitors.Dev Biol. 2015 Aug 15;404(2):2-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25779704 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Neuroglia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1175:15-44. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9913-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31583583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Solute Carrier 6 Gene Family in Silkworm (Bombyx mori).Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 3;17(10):1675. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101675. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27706106 Free PMC article.
-
Physiology of Astroglia.Physiol Rev. 2018 Jan 1;98(1):239-389. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00042.2016. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29351512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila melanogaster as a genetic model system to study neurotransmitter transporters.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jul;73:71-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.03.015. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24704795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akerman CJ, Cline HT. Refining the roles of GABAergic signaling during neural circuit formation. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:382–389. - PubMed
-
- Barbin G, Pollard H, Gaïarsa JL, Ben-Ari Y. Involvement of GABAA receptors in the outgrowth of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1993;152:150–154. - PubMed
-
- Barker JL, Behar T, Li YX, Liu QY, Ma W, Maric D, Maric I, Schaffner AE, Serafini R, Smith SV, Somogyi R, Vautrin JY, Wen XL, Xian H. GABAergic cells and signals in CNS development. Perspect Dev Neurobiol. 1998;5:305–322. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory acitons of GABA during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

