A luminescence lifetime assisted ratiometric fluorimeter for biological applications
- PMID: 20059156
- PMCID: PMC2803713
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3264106
A luminescence lifetime assisted ratiometric fluorimeter for biological applications
Abstract
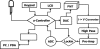
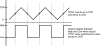
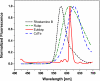
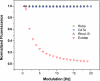
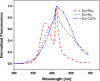
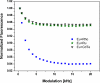
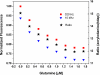
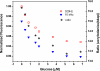
In general, the most difficult task in developing devices for fluorescence ratiometric sensing is the isolation of signals from overlapping emission wavelengths. Wavelength discrimination can be achieved by using monochromators or bandpass filters, which often lead to decreased signal intensities. The result is a device that is both complex and expensive. Here we present an alternative system--a low-cost standalone optical fluorimeter based on luminescence lifetime assisted ratiometric sensing (LARS). This paper describes the principle of this technique and the overall design of the sensor device. The most significant innovation of LARS is the ability to discriminate between two overlapping luminescence signals based on differences in their luminescence decay rates. Thus, minimal filtering is required and the two signals can be isolated despite significant overlap of luminescence spectra. The result is a device that is both simple and inexpensive. The electronic circuit employs the lock-in amplification technique for the signal processing and the system is controlled by an onboard microcontroller. In addition, the system is designed to communicate with external devices via Bluetooth.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Low-cost optical lifetime assisted ratiometric glutamine sensor based on glutamine binding protein.Anal Biochem. 2008 Dec 1;383(1):61-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.08.018. Epub 2008 Aug 26. Anal Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18786501 Free PMC article.
-
A portable time-domain LED fluorimeter for nanosecond fluorescence lifetime measurements.Rev Sci Instrum. 2014 May;85(5):055003. doi: 10.1063/1.4873330. Rev Sci Instrum. 2014. PMID: 24880404
-
A novel homogeneous bioluminescence resonance energy transfer element for biomolecular detection with CCD camera or CMOS device.Luminescence. 2008 Jan-Feb;23(1):22-7. doi: 10.1002/bio.1011. Luminescence. 2008. PMID: 18167056
-
A unique charge-coupled device/xenon arc lamp based imaging system for the accurate detection and quantitation of multicolour fluorescence.Electrophoresis. 2001 Mar;22(5):829-36. doi: 10.1002/1522-2683()22:5<829::AID-ELPS829>3.0.CO;2-U. Electrophoresis. 2001. PMID: 11332749 Review.
-
On the design of low-cost fluorescent protein biosensors.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2009;116:143-57. doi: 10.1007/10_2008_39. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19347267 Review.
References
-
- Laczko G., Gryczynsky I., Wiczk W., Malak H., and Lakowicz J. R., Rev. Sci. Instrum. RSINAK 61, 2331 (1990).10.1063/1.1141360 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

