Office-based dynamic imaging of vocal cords in awake patients with swept-source optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 20059258
- PMCID: PMC2799494
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3268442
Office-based dynamic imaging of vocal cords in awake patients with swept-source optical coherence tomography
Abstract
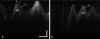
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an evolving noninvasive imaging modality that has been used to image the human larynx during surgical endoscopy. The design of a long gradient index (GRIN) lens-based probe capable of capturing images of the human larynx by use of swept-source OCT during a typical office-based laryngoscopy examination is presented. In vivo OCT imaging of the human larynx is demonstrated with a rate of 40 frames per second. Dynamic vibration of the vocal folds is recorded to provide not only high-resolution cross-sectional tissue structures but also vibration parameters, such as the vibration frequency and magnitude of the vocal cords, which provides important information for clinical diagnosis and treatment, as well as fundamental research of the voice itself. Office-based OCT is a promising imaging modality to study the larynx for physicians in otolaryngology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gradient-index lens rod based probe for office-based optical coherence tomography of the human larynx.J Biomed Opt. 2009 Jan-Feb;14(1):014017. doi: 10.1117/1.3076198. J Biomed Opt. 2009. PMID: 19256705 Free PMC article.
-
Office-based optical coherence tomographic imaging of human vocal cords.J Biomed Opt. 2006 May-Jun;11(3):30501. doi: 10.1117/1.2200371. J Biomed Opt. 2006. PMID: 16822047
-
In vivo cross-sectional imaging of the phonating larynx using long-range Doppler optical coherence tomography.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 10;6:22792. doi: 10.1038/srep22792. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26960250 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography: imaging the larynx.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012 Dec;20(6):477-81. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e3283582d7d. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012. PMID: 22913932 Review.
-
Optical coherence tomography for rapid tissue screening and directed histological sectioning.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2012;35(3):129-43. doi: 10.3233/ACP-2011-0047. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2012. PMID: 22133731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Automated working distance adjustment enables optical coherence tomography of the human larynx in awake patients.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2015 Apr;2(2):026003. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.2.2.026003. Epub 2015 Jun 25. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2015. PMID: 26158116 Free PMC article.
-
A forward-imaging needle-type OCT probe for image guided stereotactic procedures.Opt Express. 2011 Dec 19;19(27):26283-94. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.026283. Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 22274213 Free PMC article.
-
Towards OCT-Guided Endoscopic Laser Surgery-A Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 11;13(4):677. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040677. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging vibrating vocal folds with a high speed 1050 nm swept source OCT and ODT.Opt Express. 2011 Jun 6;19(12):11880-9. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.011880. Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 21716421 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronized, concurrent optical coherence tomography and videostroboscopy for monitoring vocal fold morphology and kinematics.Biomed Opt Express. 2019 Aug 6;10(9):4450-4461. doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.004450. eCollection 2019 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2019. PMID: 31565501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong B. J. F., Jackson R. P., Guo S., Ridgway J. M., Mahmood U., Su J., Shibuya T. Y., Crumley R. L., Gu M., Armstrong W. B., and Chen Z., “In vivo optical coherence tomography of the human larynx: normative and benign pathology in 82 patients,” Laryngoscope LARYA8 115, 1904–1911 (2005).10.1097/01.MLG.0000181465.17744.BE - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sergeev A. M., Gelikonov V. M., Gelikonov G. V., Feldchtein F., Kuranov R., Gladkova N., Shakhova N., Snopova L., Shakhov A., Kuznetsova I., Denisenko A., Pochinko V., Chumakov Yu., and Streltzova O., “In vivo endoscopic OCT imaging of precancer and cancer states of human mucosa,” Opt. Express OPEXFF 1, 432–440 (1997).10.1364/OE.1.000432 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luerssen K., Lubatschowski H., Gasse H., Koch R., and Ptok M., “Optical characterization of vocal folds with optical coherence tomography,” Proc. SPIE PSISDG 5686, 328–332 (2005).10.1117/12.592630 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

