Molecular diagnosis and therapy of kidney cancer
- PMID: 20059341
- PMCID: PMC2921612
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.med.042808.171650
Molecular diagnosis and therapy of kidney cancer
Abstract
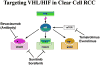
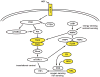
Kidney cancer is not a single disease; it is made up of a number of cancers that occur in the kidney, each having a different histology, following a different clinical course, responding differently to therapy, and caused by a different gene. Study of the genes underlying kidney cancer has revealed that it is fundamentally a metabolic disorder. Understanding the genetic basis of cancer of the kidney has significant implications for diagnosis and management of this disease. VHL is the gene for clear cell kidney cancer. The VHL protein forms a complex that targets the hypoxia-inducible factors for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Knowledge of this pathway provided the foundation for the development of novel therapeutic approaches now approved for treatment of this disease. MET is the gene for the hereditary form of type 1 papillary renal carcinoma and is mutated in a subset of sporadic type 1 papillary kidney cancers. Clinical trials are currently ongoing with agents targeting the tyrosine kinase domain of MET in sporadic and hereditary forms of papillary kidney cancer. BHD is the gene for the hereditary type of chromophobe kidney cancer. It is thought to be involved in energy and/or nutrient sensing through the AMPK and mTOR signaling pathways. Hereditary leiomyomatosis renal cell carcinoma, a hereditary form of type 2 papillary renal carcinoma, is caused by inactivation of a Krebs cycle enzyme due to mutation. Knowledge of these kidney cancer gene pathways has enabled new approaches in the management of this disease and has provided the foundation for the development of targeted therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The genetic basis of kidney cancer: a metabolic disease.Nat Rev Urol. 2010 May;7(5):277-85. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2010.47. Nat Rev Urol. 2010. PMID: 20448661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic basis of cancer of the kidney: disease-specific approaches to therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep 15;10(18 Pt 2):6282S-9S. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-050013. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15448018 Review.
-
Genetic basis for kidney cancer: opportunity for disease-specific approaches to therapy.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008 Jun;8(6):779-90. doi: 10.1517/14712598.8.6.779. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18476789 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic basis of cancer of the kidney.J Urol. 2003 Dec;170(6 Pt 1):2163-72. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000096060.92397.ed. J Urol. 2003. PMID: 14634372 Review.
-
Hereditary kidney cancer: unique opportunity for disease-based therapy.Cancer. 2009 May 15;115(10 Suppl):2252-61. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24230. Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19402075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological features of Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma.Korean J Urol. 2015 Mar;56(3):212-7. doi: 10.4111/kju.2015.56.3.212. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Korean J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25763125 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of SIGLEC12 expression, immunomodulation and prognostic value in renal cancer using multiomic databases.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 11;10(2):e24286. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24286. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38268823 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding morphological and clinical aspects of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC): a case report in a patient with unusual morphology and clinical presentation.Virchows Arch. 2018 Dec;473(6):775-779. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2420-3. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Virchows Arch. 2018. PMID: 30171332
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome From 2001 to 2021.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 11;9:857127. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.857127. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35479937 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho suppresses tumor progression via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Snail signaling in renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2013 Jun;104(6):663-71. doi: 10.1111/cas.12134. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23433103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bui MH, Seligson D, Han KR, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is an independent predictor of survival in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:802–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

