Sequential expression of macrophage anti-microbial/inflammatory and wound healing markers following innate, alternative and classical activation
- PMID: 20059482
- PMCID: PMC2883107
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04086.x
Sequential expression of macrophage anti-microbial/inflammatory and wound healing markers following innate, alternative and classical activation
Abstract
The present study examines the temporal dynamics of macrophage activation marker expression in response to variations in stimulation. We demonstrate that markers can be categorized as 'early' (expressed most abundantly at 6 h post-stimulation) or 'late' (expressed at 24 h post-stimulation). Thus nos2 and p40 (IL-12/IL-23) are early markers of innate and classical activation, while dectin-1 and mrc-1 are early markers and fizz1 (found in inflammatory zone-1) and ym1 are late markers of alternative activation. Furthermore, argI is a late marker of both innate and alternative activation. The ability of interferon (IFN)-gamma to alter these activation markers was studied at both the protein level and gene level. As reported previously, IFN-gamma was able to drive macrophages towards the classical phenotype by enhancing nos2 gene expression and enzyme activity and p40 (IL-12/IL-23) gene expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages. IFN-gamma antagonized alternative macrophage activation, as evident by reduced expression of dectin-1, mrc-1, fizz1 and ym1 mRNA transcripts. In addition, IFN-gamma antagonized arginase activity irrespective of whether macrophages were activated innately or alternatively. Our data explain some apparent contradictions in the literature, demonstrate temporal plasticity in macrophage activation states and define for the first time 'early' and 'late' markers associated with anti-microbial/inflammatory and wound healing responses, respectively.
Figures
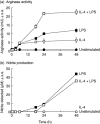
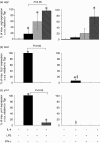
 ), or with both 100 U/ml IL-4 and 200 ng/ml LPS (□) over a 48-h time-period. Results show mean ± standard error of n = 3.
), or with both 100 U/ml IL-4 and 200 ng/ml LPS (□) over a 48-h time-period. Results show mean ± standard error of n = 3.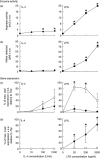
 ) for 48 h. Results show mean ± standard error (s.e.) of n = 3 samples. *P < 0·05 in comparison with unstimulated controls. argI (c) and nos2 (d) mRNA expression in BMD macrophages that have been stimulated for 6 (closed circles/squares) or 24 h (open circles/squares) with 0–1000 U/ml IL-4 (circles) or 0–2000 ng/ml LPS (squares). Expression levels for argI and nos2 mRNA transcripts were normalized to the housekeeping gene Tbp for each experimental run. The maximum gene expression for each run was designated 100% and all treatments calculated in comparison to this. Data is presented as the mean expression ± s.e. of n = 3. *P < 0·05 for values between time-points of the same treatment.
) for 48 h. Results show mean ± standard error (s.e.) of n = 3 samples. *P < 0·05 in comparison with unstimulated controls. argI (c) and nos2 (d) mRNA expression in BMD macrophages that have been stimulated for 6 (closed circles/squares) or 24 h (open circles/squares) with 0–1000 U/ml IL-4 (circles) or 0–2000 ng/ml LPS (squares). Expression levels for argI and nos2 mRNA transcripts were normalized to the housekeeping gene Tbp for each experimental run. The maximum gene expression for each run was designated 100% and all treatments calculated in comparison to this. Data is presented as the mean expression ± s.e. of n = 3. *P < 0·05 for values between time-points of the same treatment.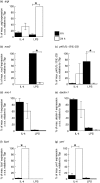

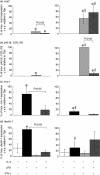
References
-
- Bogdan C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:907–16. - PubMed
-
- Willment JA, Lin HH, Reid DM, et al. Dectin-1 expression and function are enhanced on alternatively activated and GM-CSF-treated macrophages and are negatively regulated by IL-10, dexamethasone, and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 2003;171:4569–73. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:23–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

