TPH2 5'- and 3'-regulatory polymorphisms are differentially associated with HPA axis function and self-injurious behavior in rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 20059554
- PMCID: PMC2990963
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00564.x
TPH2 5'- and 3'-regulatory polymorphisms are differentially associated with HPA axis function and self-injurious behavior in rhesus monkeys
Abstract
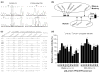
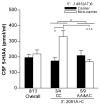
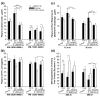
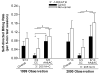
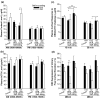
Tryptophan hydroxylase-2 (TPH2) synthesizes neuronal serotonin and is linked to numerous behavioral traits. We have previously characterized the functionality of polymorphisms (especially 2051A>C) in 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of rhesus monkey TPH2 (rhTPH2). This study further assessed the functionality of additional polymorphisms (-1605T>C, -1491Tn, -1485(AT)n, -1454A>G, -1325In>Del and -363T>G) in rhTPH2 5'-flanking region (5'-FR), and evaluated the effects of rhTPH2 5' and 3' genotypes on central serotonin turnover, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function and self-injurious behavior (SIB) in 32 unrelated adult male monkeys of Indian origin. Haplotypes of the rhTPH2 5'-FR polymorphisms exert a significant, cell-dependent effect on reporter gene expression, primarily conferred by -1485(AT)n. The -1485(AT)n and 2051A>C polymorphisms interact to influence cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 5-HIAA and plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in the afternoon. While -1485(AT)n exerts significant main effects on the afternoon cortisol level and nocturnal HPA negative feedback, 2051A>C has significant main effects on the morning cortisol level and cortisol response to ACTH challenge, as well as marginally significant main effects on the daytime HPA negative feedback and self-biting rate. In addition, the genotype/allele frequency of the 5'-FR -1325Ins>Del differed significantly between the self-wounders and non-wounders, whereas 3'-UTR 2128S>L polymorphism differed significantly in genotype/allele frequency between the high- and low-frequency biters. This study shows the functionality of rhTPH2 5'-FR polymorphisms, and provides evidence for the differential association of rhTPH2 5'-FR and 3'-UTR polymorphisms with HPA axis function and SIB. Our findings shed light on the role of TPH2 gene variance in physiology and behavioral traits, and also contribute to the understanding of the pathophysiology and genetics of SIB.
Figures
References
-
- Barr CS, Newman TK, Lindell S, Shannon C, Champoux M, Lesch KP, Suomi SJ, Goldman D, Higley JD. Interaction between serotonin transporter gene variation and rearing condition in alcohol preference and consumption in female primates. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004a;61:1146–1152. - PubMed
-
- Barr CS, Newman TK, Shannon C, Parker C, Dvoskin RL, Becker ML, Schwandt M, Champoux M, Lesch KP, Goldman D, Suomi SJ, Higley JD. Rearing condition and rh5-HTTLPR interact to influence limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response to stress in infant macaques. Biol Psychiatry. 2004b;55:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Bennett AJ, Lesch KP, Heils A, Long JC, Lorenz JG, Shoaf SE, Champoux M, Suomi SJ, Linnoila MV, Higley JD. Early experience and serotonin transporter gene variation interact to influence primate CNS function. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7:118–122. - PubMed
-
- Bentson KL, Capitanio JP, Mendoza SP. Cortisol responses to immobilization with Telazol or ketamine in baboons (Papio cynocephalus/anubis) and rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) J Med Primatol. 2003;32:148–160. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein SR, Engeland WC, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Herman JP. Dissociation of ACTH and glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2008;19:175–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24 OD011180/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R24 RR011122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA025697/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH077995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RR11122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AA016194/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- RR00168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH082507/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA016194/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR000168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH077995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA025697/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH082507/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

