1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances the ability of transferred CD4+ CD25+ cells to modulate T helper type 2-driven asthmatic responses
- PMID: 20059575
- PMCID: PMC2878463
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03222.x
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances the ability of transferred CD4+ CD25+ cells to modulate T helper type 2-driven asthmatic responses
Abstract
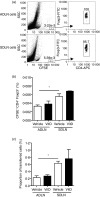
The severity of allergic diseases may be modified by vitamin D. However, the immune pathways modulated by the active form of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,25(OH)(2)D(3)], are yet to be fully elucidated. In this study, naturally occurring CD4(+) CD25(+) cells from the skin-draining lymph nodes (SDLN) of mice treated with topical 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) had an increased ability to suppress T helper type 2 (Th2) -skewed immune responses. CD4(+) CD25(+) cells transferred from mice treated with topical 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) into ovalbumin (OVA) -sensitized mice challenged intranasally with OVA 18 hr later, significantly suppressed the capacity of airway-draining lymph node (ADLN) cells to proliferate and secrete cytokines in response to further OVA stimulation ex vivo. The CD4(+) CD25(+) cells from 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-treated mice also reduced airway hyperresponsiveness and the proportions of neutrophils and eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). To test the effect of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) on cells able to respond to a specific antigen, CD4(+) CD25(+) cells were purified from the SDLN of OVA-T-cell receptor (TCR) transgenic mice treated 4 days earlier with topical 1,25(OH)(2)D(3). CD4(+) CD25(+) cells from OVA-TCR mice treated with 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) were able to alter BALF cell content and suppress ADLN responses to a similar degree to those cells from non-transgenic mice, suggesting that the effect of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) was not related to TCR signalling. In summary, topical 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) increased the regulatory capacity of CD4(+) CD25(+) cells from the SDLN to suppress Th2-mediated allergic airway disease. This work highlights how local 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) production by lung epithelial cells may modulate the suppressive activity of local regulatory T cells.
Figures





References
-
- Miyara M, Wing K, Sakaguchi S. Therapeutic approaches to allergy and autoimmunity based on Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:749–55. - PubMed
-
- Gorman S, Kuritzky LA, Judge MA, Dixon KM, McGlade JP, Mason RS, Finlay-Jones JJ, Hart PH. Topically applied 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances the suppressive activity of CD4+ CD25+ cells in the draining lymph nodes. J Immunol. 2007;179:6273–83. - PubMed
-
- Gorman S, Tan JW-Y, Yerkovich ST, Finlay-Jones JJ, Hart PH. CD4+ T cells in lymph nodes of UVB-irradiated mice suppress immune responses to new antigens both in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:915–24. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz T. 25 years of UV-induced immunosuppression mediated by T cells – from disregarded T suppressor cells to highly respected regulatory T cells. Photochem Photobiol. 2008;84:10–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

