Lipid-based nanotherapeutics for siRNA delivery
- PMID: 20059641
- PMCID: PMC5308083
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02189.x
Lipid-based nanotherapeutics for siRNA delivery
Abstract
RNA interference (RNAi) is a specific gene-silencing mechanism triggered by small interfering RNA (siRNA). The application of RNAi in the clinic requires the development of safe and effective delivery systems. Inspired by progress with lipid-based systems in drug delivery, efforts have been dedicated to the development of liposomal siRNA delivery systems. Many of the lipid-based delivery vehicles self-assemble with siRNA through electrostatic interactions with charged amines, generating multi-lamellar lipoplexes with positively charged lipid bilayers separated from one another by sheets of negatively charged siRNA strands. Internalization of lipid-based siRNA delivery systems into cells typically occurs through endocytosis; accordingly, delivery requires materials that can facilitate endosomal escape. The size of the carrier is important as carriers <100 nm in diameter have been reported to have higher accumulation levels in tumours, hepatocytes and inflamed tissue, whereas larger particles tend to be taken up by Kupffer cells or other components of the reticuloendothelial system (RES). To reduce RES uptake and increase circulation time, carriers have been modified on the surface with hydrophilic materials, such as polyethyleneglycol. Herein, we review the molecular and structural parameters of lipid-based siRNA delivery systems.
Figures
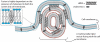

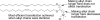
References
-
- Novina CD, Sharp PA. The RNAi revolution. Nature. 2004;430:161–4. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–11. - PubMed
-
- Hansen KM, Ji HF, Wu G, et al. Cantilever-based optical deflection assay for discrimination of DNA single-nucleotide mismatches. Anal Chem. 2001;73:1567–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

