Emerging peptide nanomedicine to regenerate tissues and organs
- PMID: 20059645
- PMCID: PMC3676424
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02184.x
Emerging peptide nanomedicine to regenerate tissues and organs
Abstract
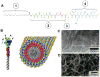
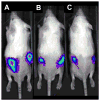
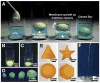
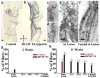
Peptide nanostructures containing bioactive signals offer exciting novel therapies of broad potential impact in regenerative medicine. These nanostructures can be designed through self-assembly strategies and supramolecular chemistry, and have the potential to combine bioactivity for multiple targets with biocompatibility. It is also possible to multiplex their functions by using them to deliver proteins, nucleic acids, drugs and cells. In this review, we illustrate progress made in this new field by our group and others using peptide-based nanotechnology. Specifically, we highlight the use of self-assembling peptide amphiphiles towards applications in the regeneration of the central nervous system, vasculature and hard tissue along with the transplant of islets and the controlled release of nitric oxide to prevent neointimal hyperplasia. Also, we discuss other self-assembling oligopeptide technology and the progress made with these materials towards the development of potential therapies.
Figures




References
-
- Gurtner GC, Callaghan MJ, Longaker MT. Progress and potential for regenerative medicine. Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:299–312. - PubMed
-
- Hartgerink JD, Beniash E, Stupp SI. Self-assembly and mineralization of peptide-amphiphile nanofibers. Science. 2001;294:1684–8. - PubMed
-
- Harrison BS, Atala A. Carbon nanotube applications for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28:344–53. - PubMed
-
- Tran PA, Zhang L, Webster TJ. Carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes in regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Jamieson T, Bakhshi R, Petrova D, Pocock R, Imani M, Seifalian AM. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials. 2007;28:4717–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

