Regulation of G-protein coupled receptor traffic by an evolutionary conserved hydrophobic signal
- PMID: 20059747
- PMCID: PMC2919199
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01033.x
Regulation of G-protein coupled receptor traffic by an evolutionary conserved hydrophobic signal
Abstract
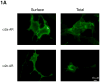
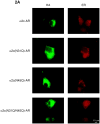
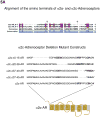
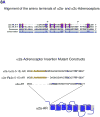
Plasma membrane (PM) expression of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) is required for activation by extracellular ligands; however, mechanisms that regulate PM expression of GPCRs are poorly understood. For some GPCRs, such as alpha2c-adrenergic receptors (alpha(2c)-ARs), heterologous expression in non-native cells results in limited PM expression and extensive endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retention. Recently, ER export/retentions signals have been proposed to regulate cellular trafficking of several GPCRs. By utilizing a chimeric alpha(2a)/alpha(2c)-AR strategy, we identified an evolutionary conserved hydrophobic sequence (ALAAALAAAAA) in the extracellular amino terminal region that is responsible in part for alpha(2c)-AR subtype-specific trafficking. To our knowledge, this is the first luminal ER retention signal reported for a GPCR. Removal or disruption of the ER retention signal dramatically increased PM expression and decreased ER retention. Conversely, transplantation of this hydrophobic sequence into alpha(2a)-ARs reduced their PM expression and increased ER retention. This evolutionary conserved hydrophobic trafficking signal within alpha(2c)-ARs serves as a regulator of GPCR trafficking.
Keywords: ER export; ER retention; GPCR trafficking; protein sorting; retention signal.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Regulation of α2B-Adrenerigc Receptor Export Trafficking by Specific Motifs.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;132:227-44. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26055061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic and quantitative analysis of G protein-coupled receptor trafficking motifs.Methods Enzymol. 2013;521:171-87. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391862-8.00009-0. Methods Enzymol. 2013. PMID: 23351739 Free PMC article.
-
REEPs are membrane shaping adapter proteins that modulate specific g protein-coupled receptor trafficking by affecting ER cargo capacity.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 2;8(10):e76366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076366. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098485 Free PMC article.
-
A single lys residue on the first intracellular loop modulates the endoplasmic reticulum export and cell-surface expression of α2A-adrenergic receptor.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050416. Epub 2012 Dec 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23227171 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory mechanisms of export trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors.Cell Signal. 2005 Dec;17(12):1457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.05.020. Cell Signal. 2005. PMID: 16014327 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel bourgeonal fragrance conjugates for the detection of prostate cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Oct;31(5):1151-7. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-9943-x. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23508273
-
Regulation of α2B-Adrenerigc Receptor Export Trafficking by Specific Motifs.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;132:227-44. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26055061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common α2A and α2C adrenergic receptor polymorphisms do not affect plasma membrane trafficking.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;387(6):569-579. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-0972-6. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24643471 Free PMC article.
-
REEP1 and REEP2 proteins are preferentially expressed in neuronal and neuronal-like exocytotic tissues.Brain Res. 2014 Jan 30;1545:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24355597 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Intracellular α2C-Adrenoceptor Surface Translocation Using Decoy Peptides: Identification of an Essential Role of the C-Terminus in Receptor Trafficking.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 16;24(24):17558. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417558. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ellgaard L, Helenius A. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(3):181–191. - PubMed
-
- Hebert DN, Garman SC, Molinari M. The glycan code of the endoplasmic reticulum: asparagine-linked carbohydrates as protein maturation and quality-control tags. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15(7):364–370. - PubMed
-
- Brady AE, Limbird LE. G protein-coupled receptor interacting proteins: emerging roles in localization and signal transduction. Cellular Signalling. 2002;14(4):297–309. - PubMed
-
- von Zastrow M, Link R, Daunt D, Barsh G, Kobilka B. Subtype-specific differences in the intracellular sorting of G protein- coupled receptors. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1993;268(2):763–766. - PubMed
-
- Daunt DA, Hurt C, Hein L, Kallio J, Feng F, Kobilka BK. Subtype-specific intracellular trafficking of alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;51(5):711–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

