Chronic antipsychotic treatment: protracted decreases in phospho-TrkA levels in the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 20059802
- PMCID: PMC4400726
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145709991040
Chronic antipsychotic treatment: protracted decreases in phospho-TrkA levels in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
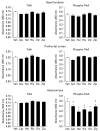
There is growing evidence of neurotrophin alterations in neuropsychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia and further, neurotransmitters known to be adversely affected in schizophrenia (e.g. dopamine) can activate neurotrophin signalling pathways via G protein-coupled receptors. However, it is unclear how the primary therapeutic agents used in schizophrenia affect neurotrophin signalling. This is important given that all currently prescribed antipsychotic drugs serve as ligands at dopamine receptors. In this study, chronic effects of representative conventional and second-generation antipsychotics on nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor levels were assessed in the rat. The results indicated no significant drug effects on TrkA levels in any brain region analysed; however, three of the five antipsychotics analysed significantly decreased phospho-TrkA (i.e. the activated form of the receptor) in the hippocampus. These data indicate that chronic antipsychotic treatment may result in deleterious effects on neurotrophin signalling in an important brain region for information processing and cognition.
Figures
References
-
- Angelucci F, Brene S, Mathe AA. BDNF in schizophrenia, depression and corresponding animal models. Molecular Psychiatry. 2005;10:345–352. - PubMed
-
- Angelucci F, Luigi A, Gruber SHM, Fiore M, et al. Chronic antipsychotic treatment selectively alters nerve growth factor and neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity and the distribution of choline acetyl transferase in rat brain regions. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000;3:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Balant-Gorgia AE, Gex-Fabry M, Genet C, Balant LP. Therapeutic drug monitoring of risperidone using a new, rapid HPLC method: reappraisal of interindividual variability factors. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. 1999;21:105–115. - PubMed
-
- Barker PA. p75NTR is positively promiscuous: novel partners and new insights. Neuron. 2004;42:529–533. - PubMed
-
- Baldessarini RJ, Cohen BM, Teicher MH. Significance of neuroleptic dose and plasma level in the pharmacological treatment of psychoses. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1988;45:79–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

