A systems approach reveals that the myogenesis genome network is regulated by the transcriptional repressor RP58
- PMID: 20059953
- PMCID: PMC3110151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.10.011
A systems approach reveals that the myogenesis genome network is regulated by the transcriptional repressor RP58
Abstract
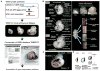
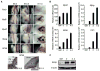
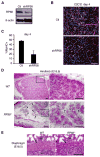
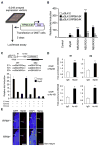
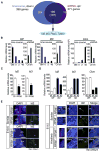
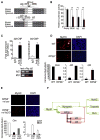
We created a whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) database, termed EMBRYS, containing expression data of 1520 transcription factors and cofactors expressed in E9.5, E10.5, and E11.5 mouse embryos--a highly dynamic stage of skeletal myogenesis. This approach implicated 43 genes in regulation of embryonic myogenesis, including a transcriptional repressor, the zinc-finger protein RP58 (also known as Zfp238). Knockout and knockdown approaches confirmed an essential role for RP58 in skeletal myogenesis. Cell-based high-throughput transfection screening revealed that RP58 is a direct MyoD target. Microarray analysis identified two inhibitors of skeletal myogenesis, Id2 and Id3, as targets for RP58-mediated repression. Consistently, MyoD-dependent activation of the myogenic program is impaired in RP58 null fibroblasts and downregulation of Id2 and Id3 rescues MyoD's ability to promote myogenesis in these cells. Our combined, multi-system approach reveals a MyoD-activated regulatory loop relying on RP58-mediated repression of muscle regulatory factor (MRF) inhibitors.
2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aoki K, Meng G, Suzuki K, Takashi T, Kameoka Y, Nakahara K, Ishida R, Kasai M. RP58 associates with condensed chromatin and mediates a sequence-specific transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:26698–26704. - PubMed
-
- Arnold HH, Braun T. Targeted inactivation of myogenic factor genes reveals their role during mouse myogenesis: a review. Int J Dev Biol. 1996;40:345–353. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990;61:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell TK, Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990;250:1104–1110. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell TK, Kretzner L, Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN, Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990;250:1149–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

