A genomic-library based discovery of a novel, possibly synthetic, acid-tolerance mechanism in Clostridium acetobutylicum involving non-coding RNAs and ribosomal RNA processing
- PMID: 20060060
- PMCID: PMC2857598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2009.12.004
A genomic-library based discovery of a novel, possibly synthetic, acid-tolerance mechanism in Clostridium acetobutylicum involving non-coding RNAs and ribosomal RNA processing
Abstract
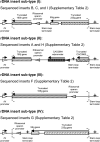
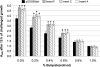
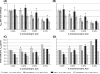
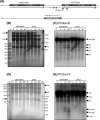
We generated a genomic library from sheared Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 DNA, whereby inserts can be expressed in both directions from the thiolase promoter, P(thl). Serial transfer of library-bearing C. acetobutylicum cultures exposed to increasing butyrate concentrations enriched for inserts containing fragments of rRNA genetic loci. The selected library inserts were placed so that antisense (to the rRNAs) non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) would be transcribed from P(thl). Different enriched inserts imparted similar butyrate-tolerance characteristics. A minimal tolerance fragment (RDNA7) was identified as the 16S-rRNA promoter region. Expressed on plasmid pRD7 off P(thl), RDNA7 can produce putative ncRNAs termed ncRNA(RD7). C. acetobutylicum 824(pRD7) showed superior resistance to butyrate and other carboxylic acids. Transcriptional analysis of butyrate stress identified 120 differentially expressed genes between 824(pRD7) and 824(pSOS95del). The few upregulated genes included the ffh gene of the putative signal recognition particle (SRP) system. Northern analysis of ncRNA(RD7) and corresponding antisense RNAs demonstrated multiple ncRNA(RD7) molecules in 824(pRD7). Several corresponding antisense RNA molecules were identified both in 824(pRD7) and 824(pSOS95del), but at much higher levels in 824(pRD7). Northern analysis of 16S rRNA expression suggested complex RDNA7-dependent rRNA processing. Our data suggest that by hybridizing against unprocessed rRNA precursors, ncRNA(RD7) alters rRNA processing, and these alterations result in acid tolerance, possibly through a mechanism involving the Ffh protein.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamics of genomic-library enrichment and identification of solvent tolerance genes for Clostridium acetobutylicum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 May;73(9):3061-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02296-06. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17337545 Free PMC article.
-
S-box and T-box riboswitches and antisense RNA control a sulfur metabolic operon of Clostridium acetobutylicum.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(18):5955-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn601. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18812398 Free PMC article.
-
Aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase and/or thiolase overexpression coupled with CoA transferase downregulation lead to higher alcohol titers and selectivity in Clostridium acetobutylicum fermentations.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009 Jan 1;102(1):38-49. doi: 10.1002/bit.22058. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009. PMID: 18726959
-
Antisense in abundance: the ribosome as a vehicle for antisense RNA.Genet Eng (N Y). 1998;20:143-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1739-3_8. Genet Eng (N Y). 1998. PMID: 9666559 Review.
-
Beyond rRNA: nucleolar transcription generates a complex network of RNAs with multiple roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2022 Aug 1;36(15-16):876-886. doi: 10.1101/gad.349969.122. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 36207140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small and Low but Potent: the Complex Regulatory Role of the Small RNA SolB in Solventogenesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jul 2;84(14):e00597-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00597-18. Print 2018 Jul 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29728392 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments of the Synthetic Biology Toolkit for Clostridium.Front Microbiol. 2018 Feb 12;9:154. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00154. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29483900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNAs in the genus Clostridium.mBio. 2011 Jan 25;2(1):e00340-10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00340-10. mBio. 2011. PMID: 21264064 Free PMC article.
-
Group II intron-anchored gene deletion in Clostridium.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 31;6(1):e16693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016693. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21304965 Free PMC article.
-
Small genes under sporulation control in the Bacillus subtilis genome.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(20):5402-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00534-10. Epub 2010 Aug 13. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20709900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsaker KV, et al. Design, optimization and validation of genomic DNA microarraysfor examining the Clostridium acetobutylicum transcriptome. Biotechnol. BioprocessEng. 2005;10:432–443.
-
- Ballal A, et al. The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007;32:559–68. - PubMed
-
- Bouvier M, et al. Small RNA binding to 5′ mRNA coding region inhibits translational initiation. Mol. Cell. 2008;32:827–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

