Gluten-free diet and steroid treatment are effective therapy for most patients with collagenous sprue
- PMID: 20060071
- PMCID: PMC3493150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.12.023
Gluten-free diet and steroid treatment are effective therapy for most patients with collagenous sprue
Abstract
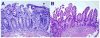
Background & aims: Collagenous sprue (CS) is characterized by the presence of a distinctive band of subepithelial collagen deposition in the small bowel. We evaluated the clinical characteristics, treatments, and outcomes of patients with CS.
Methods: Thirty patients with CS were identified at the 3 Mayo Clinic sites between 1993 and 2009. Clinical data from medical records were reviewed.
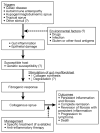
Results: The study cohort was 70% female (age range, 53-91 years). Most patients had severe diarrhea and weight loss. Hospitalization to treat dehydration was necessary in 16 (53%) patients. Associated immune-mediated diseases were noted in 70% of the patients; celiac disease was the most frequent. Other associated diseases were microscopic colitis, hypothyroidism, and autoimmune enteropathy. The median thickness of the layer of subepithelial collagen deposition in the small bowel was 29 mum (20-56.5 mum). Subepithelial collagen deposition in the colon or stomach was noted in 8 patients. A clinical response was observed in 24 (80%) patients after treatment with a combination of a gluten-free diet and immunosuppressive drugs. Histologic improvement was confirmed in 9 patients, with complete remission in 5. Two patients died (1 of complications of CS and 1 of another illness).
Conclusions: Most patients with CS are treated effectively with a combination of gluten-free diet and steroids. CS is often associated with collagen deposition or chronic inflammation in other segments of the gastrointestinal tract as well as other immune-mediated disorders.
Copyright 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Weinstein WM, Saunders DR, Tytgat GN, et al. Collagenous sprue: an unrecognized type of malabsorption. N Engl J Med. 1970;283:1297–1301. - PubMed
-
- Brandborg LL. Histologic diagnosis of diseases of malabsorption. Am J Med. 1979;67:999–1006. - PubMed
-
- Schein J. Syndrome of non tropical sprue with hitherto undescribed lesions of the intestine. Gastroenterology. 1947;8:438–460. - PubMed
-
- Pepper HW, Brandborg LL, Shanser JD, et al. Collagenous sprue. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974;121:275–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

