Spatiotemporal characterization of ionizing radiation induced DNA damage foci and their relation to chromatin organization
- PMID: 20060491
- PMCID: PMC3951968
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2009.12.006
Spatiotemporal characterization of ionizing radiation induced DNA damage foci and their relation to chromatin organization
Abstract
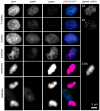
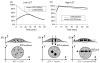
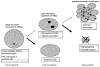
DNA damage sensing proteins have been shown to localize to the sites of DNA double strand breaks (DSB) within seconds to minutes following ionizing radiation (IR) exposure, resulting in the formation of microscopically visible nuclear domains referred to as radiation-induced foci (RIF). This review characterizes the spatiotemporal properties of RIF at physiological doses, minutes to hours following exposure to ionizing radiation, and it proposes a model describing RIF formation and resolution as a function of radiation quality and chromatin territories. Discussion is limited to RIF formed by three interrelated proteins ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated), 53BP1 (p53 binding protein 1) and gammaH2AX (phosphorylated variant histone H2AX), with an emphasis on the later. This review discusses the importance of not equating RIF with DSB in all situations and shows how dose and time dependence of RIF frequency is inconsistent with a one to one equivalence. Instead, we propose that RIF mark regions of the chromatin that would serve as scaffolds rigid enough to keep broken DNA from diffusing away, but open enough to allow the repair machinery to access the damage site. We review data indicating clear kinetic and physical differences between RIF emerging from dense and uncondensed regions of the nucleus. We suggest that persistent RIF observed days following exposure to ionizing radiation are nuclear marks of permanent rearrangement of the chromatin architecture. Such chromatin alterations may not always lead to growth arrest as cells have been shown to replicate these in progeny. Thus, heritable persistent RIF spanning over tens of Mbp may reflect persistent changes in the transcriptome of a large progeny of cells. Such model opens the door to a "non-DNA-centric view" of radiation-induced phenotypes.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Ashley T, Plug AW, Xu J, Solari AJ, Reddy G, Golub EI, Ward DC. Dynamic changes in Rad51 distribution on chromatin during meiosis in male and female vertebrates. Chromosoma. 1995;104:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Nelms BE, Maser RS, MacKay JF, Lagally MG, Petrini JH. In situ visualization of DNA double-strand break repair in human fibroblasts. Science. 1998;280:590–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

