The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription?
- PMID: 20060942
- PMCID: PMC2862274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.001
The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription?
Abstract
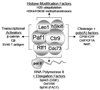
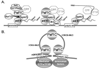
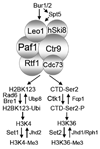
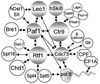
The Paf1 complex (Paf1C), composed of the proteins Paf1, Ctr9, Cdc73, Rtf1, and Leo1, accompanies RNA polymerase II (pol II) from the promoter to the 3' end formation site of mRNA and snoRNA encoding genes; it is also found associated with RNA polymerase I (pol I) on rDNA. The Paf1C is found in simple and complex eukaryotes; in human cells hSki8 is also part of the complex. The Paf1C has been linked to a large and growing list of transcription related processes including: communication with transcriptional activators; recruitment and activation of histone modification factors; facilitation of elongation on chromatin templates; and the recruitment of 3' end-processing factors necessary for accurate termination of transcription. Absence of, or mutations in, Paf1C factors result in alterations in gene expression that can result in misregulation of developmental programs and loss of control of cell division leading to cancer in humans. This review considers recent information that may help to resolve whether the Paf1C is primarily a "platform" on pol II that coordinates the association of many critical transcription factors, or if the complex itself plays a more direct role in one or more steps in transcription.
Figures
References
-
- Wade PA, Werel W, Fentzke RC, Thompson NE, Leykam JF, Burgess RR, Jaehning JA, Burton ZF. A novel collection of accessory factors associated with yeast RNA polymerase II. Protein Expr. Purif. 1996;8:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Kim YJ, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre MH, Kornberg RD. A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994;77:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Koleske AJ, Young RA. An RNA polymerase II holoenzyme responsive to activators. Nature. 1994;368:466–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

