Genome-wide identification of hypoxia-inducible factor binding sites and target genes by a probabilistic model integrating transcription-profiling data and in silico binding site prediction
- PMID: 20061373
- PMCID: PMC2853119
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1205
Genome-wide identification of hypoxia-inducible factor binding sites and target genes by a probabilistic model integrating transcription-profiling data and in silico binding site prediction
Abstract
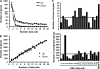
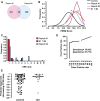
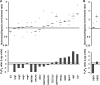
The transcriptional response driven by Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is central to the adaptation to oxygen restriction. Hence, the complete identification of HIF targets is essential for understanding the cellular responses to hypoxia. Herein we describe a computational strategy based on the combination of phylogenetic footprinting and transcription profiling meta-analysis for the identification of HIF-target genes. Comparison of the resulting candidates with published HIF1a genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation indicates a high sensitivity (78%) and specificity (97.8%). To validate our strategy, we performed HIF1a chromatin immunoprecipitation on a set of putative targets. Our results confirm the robustness of the computational strategy in predicting HIF-binding sites and reveal several novel HIF targets, including RE1-silencing transcription factor co-repressor (RCOR2). In addition, mapping of described polymorphisms to the predicted HIF-binding sites identified several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that could alter HIF binding. As a proof of principle, we demonstrate that SNP rs17004038, mapping to a functional hypoxia response element in the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) locus, prevents induction of this gene by hypoxia. Altogether, our results show that the proposed strategy is a powerful tool for the identification of HIF direct targets that expands our knowledge of the cellular adaptation to hypoxia and provides cues on the inter-individual variation in this response.
Figures


References
-
- Wenger RH, Stiehl DP, Camenisch G. Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci. STKE. 2005;2005:re12. - PubMed
-
- Salceda S, Beck I, Caro J. Absolute requirement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator protein for gene activation by hypoxia. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996;334:389–394. - PubMed
-
- Salceda S, Caro J. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:22642–22647. - PubMed
-
- Jiang BH, Zheng JZ, Leung SW, Roe R, Semenza GL. Transactivation and inhibitory domains of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Modulation of transcriptional activity by oxygen tension. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:19253–19260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

