Curcumin inhibits fibrosis-related effects in IPF fibroblasts and in mice following bleomycin-induced lung injury
- PMID: 20061443
- PMCID: PMC2867399
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00002.2009
Curcumin inhibits fibrosis-related effects in IPF fibroblasts and in mice following bleomycin-induced lung injury
Abstract
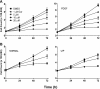
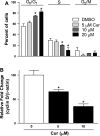
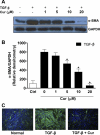
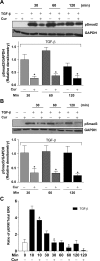
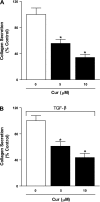
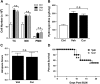
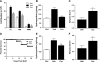
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and typically fatal lung disease for which no effective therapy has been identified. The disease is characterized by excessive collagen deposition, possibly in response to dysregulated wound healing. Mediators normally involved in would healing induce proliferation of fibroblasts and their differentiation to myofibroblasts that actively secrete collagen. Curcumin, a polyphenolic compound from turmeric, has been shown to exert a variety of biological effects. Effects on IPF and associated cell types remain unclear, however. We accordingly tested the ability of curcumin to inhibit proliferation and differentiation to myofibroblasts by human lung fibroblasts, including those from IPF patients. To further examine the potential usefulness of curcumin in IPF, we examined its ability to reduce fibrosis in bleomycin-treated mice. We show that curcumin effectively reduces profibrotic effects in both normal and IPF fibroblasts in vitro and that this reduction is accompanied by inhibition of key steps in the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway. In vivo, oral curcumin treatment showed no effect on important measures of bleomycin-induced injury in mice, whereas intraperitoneal curcumin administration effectively inhibited inflammation and collagen deposition along with a trend toward improved survival. Intraperitoneal curcumin reduced fibrotic progression even when administered after the acute bleomycin-induced inflammation had subsided. These results encourage further research on alternative formulations and routes of administration for this potentially attractive IPF therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Batth BK, Tripathi R, Srinivas UK. Curcumin-induced differentiation of mouse embryonal carcinoma PCC4 cells. Differentiation 68: 133–140, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Burgess HA, Daugherty LE, Thatcher TH, Lakatos HF, Ray DM, Redonnet M, Phipps RP, Sime PJ. PPARγ agonists inhibit TGF-β induced pulmonary myofibroblast differentiation and collagen production: implications for therapy of lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L1146–L1153, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chen YR, Tan TH. Inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway by curcumin. Oncogene 17: 173–178, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Ping J, Liu C, Tan YZ, Chen GF. Study on effects of extracts from Salvia miltiorrhiza and Curcuma longa in inhibiting phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase expression in rat's hepatic stellate cells. Chin J Integr Med 12: 207–211, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

