Characterization of a thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima
- PMID: 20061476
- PMCID: PMC2820846
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01035-09
Characterization of a thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima
Abstract
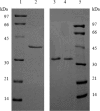
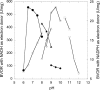
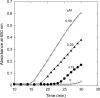
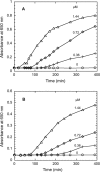
A thioredoxin reductase and a thioredoxin were purified to homogeneity from a cell extract of Thermotoga maritima. The thioredoxin reductase was a homodimeric flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-containing protein with a subunit of 37 kDa estimated using SDS-PAGE, which was identified to be TM0869. The amino acid sequence of the enzyme showed high identities and similarities to those of typical bacterial thioredoxin reductases. Although the purified T. maritima thioredoxin reductase could not use thioredoxin from Spirulina as an electron acceptor, it used thioredoxin that was purified from T. maritima by monitoring the dithiothreitol-dependent reduction of bovine insulin. This enzyme also catalyzed the reduction of benzyl viologen using NADH or NADPH as an electron donor with apparent V(max) values of 1,111 +/- 35 micromol NADH oxidized min(-1)mg(-1) and 115 +/- 2.4 micromol NADPH oxidized min(-1)mg(-1), respectively. The apparent K(m) values were determined to be 89 +/- 1.1 microM, 73 +/- 1.6 microM, and 780 +/- 20 microM for benzyl viologen, NADH, and NADPH, respectively. Optimal pH values were determined to be 9.5 and 6.5 for NADH and NADPH, respectively. The enzyme activity increased along with the rise of temperature up to 95 degrees C, and more than 60% of the activity remained after incubation for 28 h at 80 degrees C. The purified T. maritima thioredoxin was a monomer with a molecular mass of 31 kDa estimated using SDS-PAGE and identified as TM0868, which exhibited both thioredoxin and thioltransferase activities. T. maritima thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase together were able to reduce insulin or 5,5'-dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) using NAD(P)H as an electron donor. This is the first thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system characterized from hyperthermophilic bacteria.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In the absence of thioredoxins, what are the reductants for peroxiredoxins in Thermotoga maritima?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 May 1;18(13):1613-22. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4739. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22866991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Deinococcus radiophilus thioredoxin reductase active with both NADH and NADPH.J Microbiol. 2010 Oct;48(5):637-43. doi: 10.1007/s12275-010-0283-7. Epub 2010 Nov 3. J Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21046342
-
Identification and characterization of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase from Aeropyrum pernix K1.Eur J Biochem. 2002 Nov;269(22):5423-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03231.x. Eur J Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12423340
-
Quinone- and nitroreductase reactions of Thermotoga maritima thioredoxin reductase.Acta Biochim Pol. 2015;62(2):303-9. doi: 10.18388/abp.2015_1003. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Acta Biochim Pol. 2015. PMID: 26098718
-
Spectrophotometric assays for measuring redox biomarkers in blood and tissues: the NADPH network.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):47-56. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1392695. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29088980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel thermostable and halophilic thioredoxin reductase from the Red Sea Atlantis II hot brine pool.PLoS One. 2019 May 31;14(5):e0217565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217565. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31150456 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Multiple Soluble Fe(III) Reductases in Gram-Positive Thermophilic Bacterium Thermoanaerobacter indiensis BSB-33.Int J Genomics. 2014;2014:850607. doi: 10.1155/2014/850607. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Int J Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25180173 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the thioredoxin system from Methanosarcina acetivorans.FEBS J. 2014 Oct;281(20):4598-611. doi: 10.1111/febs.12964. Epub 2014 Sep 6. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 25112424 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of acetohydroxyacid synthase from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015 Aug 28;4:89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.08.014. eCollection 2015 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015. PMID: 29124191 Free PMC article.
-
In the absence of thioredoxins, what are the reductants for peroxiredoxins in Thermotoga maritima?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 May 1;18(13):1613-22. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4739. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22866991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnér, E. S. J., and A. Holmgren. 2000. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:6102-6109. - PubMed
-
- Arnér, E. S. J., J. Nordberg, and A. Holmgren. 1996. Efficient reduction of lipoamide and lipoic acid by mammalian thioredoxin reductase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 225:268-274. - PubMed
-
- Arnér, E. S. J., L. Zhong, A. Holmgren, and P. Lester. 1999. Preparation and assay of mammalian thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Methods Enzymol. 300:226-239. - PubMed
-
- Baker, A., C. M. Payne, M. M. Briehl, and G. Powis. 1997. Thioredoxin, a gene found overexpressed in human cancer, inhibits apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 57:5162-5167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

