Modified 3-oxoadipate pathway for the biodegradation of methylaromatics in Pseudomonas reinekei MT1
- PMID: 20061479
- PMCID: PMC2832525
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01208-09
Modified 3-oxoadipate pathway for the biodegradation of methylaromatics in Pseudomonas reinekei MT1
Abstract
Catechols are central intermediates in the metabolism of aromatic compounds. Degradation of 4-methylcatechol via intradiol cleavage usually leads to the formation of 4-methylmuconolactone (4-ML) as a dead-end metabolite. Only a few microorganisms are known to mineralize 4-ML. The mml gene cluster of Pseudomonas reinekei MT1, which encodes enzymes involved in the metabolism of 4-ML, is shown here to encode 10 genes found in a 9.4-kb chromosomal region. Reverse transcription assays revealed that these genes form a single operon, where their expression is controlled by two promoters. Promoter fusion assays identified 4-methyl-3-oxoadipate as an inducer. Mineralization of 4-ML is initiated by the 4-methylmuconolactone methylisomerase encoded by mmlI. This reaction produces 3-ML and is followed by a rearrangement of the double bond catalyzed by the methylmuconolactone isomerase encoded by mmlJ. Deletion of mmlL, encoding a protein of the metallo-beta-lactamase superfamily, resulted in a loss of the capability of the strain MT1 to open the lactone ring, suggesting its function as a 4-methyl-3-oxoadipate enol-lactone hydrolase. Further metabolism can be assumed to occur by analogy with reactions known from the 3-oxoadipate pathway. mmlF and mmlG probably encode a 4-methyl-3-oxoadipyl-coenzyme A (CoA) transferase, and the mmlC gene product functions as a thiolase, transforming 4-methyl-3-oxoadipyl-CoA into methylsuccinyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA, as indicated by the accumulation of 4-methyl-3-oxoadipate in the respective deletion mutant. Accumulation of methylsuccinate by an mmlK deletion mutant indicates that the encoded acetyl-CoA hydrolase/transferase is crucial for channeling methylsuccinate into the central metabolism.
Figures

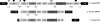
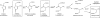
References
-
- Alber, B. E., R. R. Spanheimer, C. Ebenau-Jehle, and G. Fuchs. 2006. Study of an alternate glyoxylate cycle for acetate assimilation by Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Mol. Microbiol. 61:297-309. - PubMed
-
- Altenschmidt, U., and G. Fuchs. 1992. Novel aerobic 2-aminobenzoate metabolism. Purification and characterization of 2-aminobenzoate-CoA ligase, localisation of the genes on a 8-kbp plasmid, and cloning and sequencing of the genes from a denitrifying Pseudomonas sp. Eur. J. Biochem. 205:721-727. - PubMed
-
- Bruce, N. C., and R. B. Cain. 1988. β-Methylmuconolactone, a key intermediate in the dissimilation of methylaromatic compounds by a modified 3-oxoadipate pathway evolved in nocardioform actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 50:233-239.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

