N-acetylcysteine prevents 4-hydroxynonenal- and amyloid-beta-induced modification and inactivation of neprilysin in SH-SY5Y cells
- PMID: 20061637
- PMCID: PMC4246496
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1226
N-acetylcysteine prevents 4-hydroxynonenal- and amyloid-beta-induced modification and inactivation of neprilysin in SH-SY5Y cells
Abstract
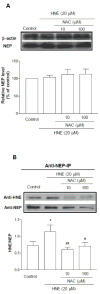
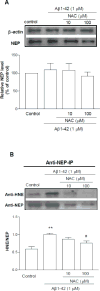
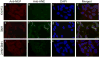
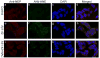
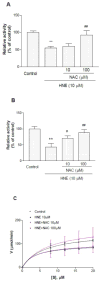
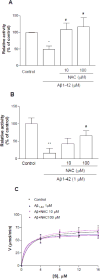
As one of the dominant amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) proteases, neprilysin (NEP) plays a crucial role in maintaining a physiologic balance between Abeta production and catabolism. We have previously shown that NEP is modified by 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) adducts, resulting in decreased activity in the brain of AD patients and cultured cells. In order to determine whether antioxidants can rescue NEP, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with HNE or Abeta, together with N-acetylcysteine for 24 hours, prior to analysis of NEP protein levels, activity, and oxidative modifications. Intracellular NEP developed HNE adducts after 24 hours of HNE or Abeta treatment as determined by immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and double immunofluorescence staining. N-acetylcysteine at 10 to 100 microM alleviated HNE adduction after HNE or Abeta treatment. In keeping with previous reports, HNE-modified NEP showed decreased catalytic activity. The present study demonstrates that antioxidants can be used to spare NEP from oxidative modification, suggesting a potential mechanism underlying the neuroprotective effects of antioxidants in aging or Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
References
-
- Areosa SA, Sherriff F. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003:CD003154. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741–766. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

