High level expression of functional human IgMs in human PER.C6 cells
- PMID: 20061826
- PMCID: PMC2725415
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.1.2.7945
High level expression of functional human IgMs in human PER.C6 cells
Abstract
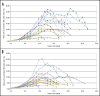
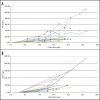
Natural IgM antibodies play an important role in the body's defense mechanisms against transformed cells in the human body and are currently being exploited both in prognoses of malignant lesions and in the therapy of cancer patients. However, despite growing interest and clinical promise, thus far the IgM class of antibodies has failed to gain widespread commercial interest as these are considered to be difficult to produce recombinantly. IgMs are polymeric and have a relatively large mass. In addition, IgM molecules are heavily glycosylated and, when produced in non-human cell lines, they may contain non-human glycan structures which may be potentially immunogenic. Clearly, production systems capable of expressing human recombinant IgM antibodies are needed. We have successfully used PER.C6 cells-a human cell line-to generate three separate human recombinant monoclonal IgMs in suspension cultures in protein-free medium. All three of the IgMs were constructed with joining (J) chain and were expressed in the pentameric form. One of the IgMs was also expressed as a hexamer without J chain. Clones with cell specific productivities greater than 20 pg/cell/day were generated, which led to yields of 0.5 g/L to 2g/L in fed-batch production. All the IgMs expressed were biologically active as shown in binding and cytotoxicity assays. These studies demonstrate the potential of PER.C6 cells for the production of high levels of functional recombinant IgM and other polymeric molecules, using a straightforward and rapid stable cell line generation method.
Figures


References
-
- Kohler G, Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975;256:495–497. - PubMed
-
- Reichert JM, Valge-Archer VE. Development trends for monoclonal antibody cancer therapeutics. Nature Reviews. 2007;6:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Collins C, Tsui FWL, Shulman MJ. Differential activation of human and guinea pig complement by pentameric and hexameric IgM. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:1802–1810. - PubMed
-
- Wiersma EJ, Collins C, Fazel S, Shulman MJ. Structural and functional analysis of J chain-deficient IgM. J Immunol. 1998;160:5979–5989. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
