Multifunctional photopolymerized semiinterpenetrating network (sIPN) system containing bupivacaine and silver sulfadiazine is an effective donor site treatment in a swine model
- PMID: 20061849
- PMCID: PMC2924184
- DOI: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3181cb8f27
Multifunctional photopolymerized semiinterpenetrating network (sIPN) system containing bupivacaine and silver sulfadiazine is an effective donor site treatment in a swine model
Abstract
Previously, we have shown in a cross-comparison study that multifunctional photopolymerized semiinterpenetrating network (sIPN) system is an effective donor site treatment in a swine model. The advantages of sIPN include spray-on application, in situ photopolymerization, and ability to cover large contoured areas. sIPN has also been shown to be an effective delivery vehicle for keratinocyte growth factor, dexamethasone, bupivacaine, and silver sulfadiazine in vitro. Our aim for this study was to show that these products delivered to the wound bed with sIPN would not change the wound healing characteristics compared with the control site through qualitative clinical evaluation and to compare the rate and quality of donor site healing through histologic evaluation. Eight Yucatan swine of 40 lbs each were randomly divided into four groups of two pigs before surgery. Each animal had 5.6% TBSA of skin harvested from two different dorsal regions, with one at 22/1000th-inch and the other at 30/1000th-inch setting on the dermatome. Each test site on each animal was then sequentially dressed with 50 cm(2) of Xeroform gauze, sIPN, sIPN loaded with 0.5% bupivacaine, or sIPN loaded with 1% silver sulfadiazine. sIPN with or without soluble drugs were applied as liquid, then photopolymerized in situ to form an elastic covering. Each of the test areas was separated by 50 cm(2) of autograft, which was used to divide the test areas. Wound assessment and killing occurred at days 7, 9, 14, and 21. A full-thickness biopsy was taken from each of the study areas for histological analysis. By 14 days, all areas showed complete epidermal coverage histologically. The 30/1000th-inch site revealed a thicker, more irregular dermis compared with the 22/1000th-site. Evaluation of the day-21 sites revealed equal thinning and flattening of the new epidermis. No site showed full restoration of the rete ridges. No signs of infection were seen in clinical or histological evaluations of any treatment. The addition of bupivacaine and silver sulfadiazine to sIPN does not show any alterations in wound healing of a donor site in a swine model when compared with sIPN without loaded drugs and a standard control dressing. This efficacy may be coupled with established localized sIPN drug delivery profiles and allow further studies to evaluate the efficacy of these drugs to promote healing, eradicate and prevent infection, and manage pain.
Figures

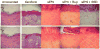



 ), 14 (
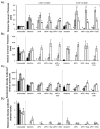
), 14 ( ), and 21 (□) days. The 0.016 in dermatome cut depth wounds are shown on the left, whereas 0.022 in wounds are on the right. Thickness of stratum spinosum(A), thickness of stratum corneum(C), viable keratinocyte density within epidermis(C), and melanocyte density(D) are displayed. Data is reported as average of 10 total viewing regions from biopsies of two separate pigs ± standard error. “X” indicates significant difference from Xeroform™ treated tissue, and “S” indicates significant difference from sIPN without drug treatment (P<0.05).
), and 21 (□) days. The 0.016 in dermatome cut depth wounds are shown on the left, whereas 0.022 in wounds are on the right. Thickness of stratum spinosum(A), thickness of stratum corneum(C), viable keratinocyte density within epidermis(C), and melanocyte density(D) are displayed. Data is reported as average of 10 total viewing regions from biopsies of two separate pigs ± standard error. “X” indicates significant difference from Xeroform™ treated tissue, and “S” indicates significant difference from sIPN without drug treatment (P<0.05).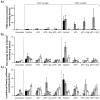
 ), 14 (
), 14 ( ), and 21 (□) days. The 0.016 in dermatome cut depth wounds are shown on the left, whereas 0.022 in wounds are on the right. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) density (including neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils) (A), macrophage density(B), and lymphocyte density(C) are displayed. Data is reported as average of 10 total viewing regions from biopsies of two separate pigs ± standard error. “X” indicates significant difference from Xeroform™ treated tissue, and “S” indicates significant difference from sIPN without drug treatment (P<0.05).
), and 21 (□) days. The 0.016 in dermatome cut depth wounds are shown on the left, whereas 0.022 in wounds are on the right. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) density (including neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils) (A), macrophage density(B), and lymphocyte density(C) are displayed. Data is reported as average of 10 total viewing regions from biopsies of two separate pigs ± standard error. “X” indicates significant difference from Xeroform™ treated tissue, and “S” indicates significant difference from sIPN without drug treatment (P<0.05).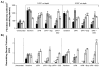
 ), 14 (
), 14 ( ), and 21 (□) days. The 0.016 in dermatome cut depth wounds are shown on the left, whereas 0.022 in wounds are on the right. Fibroblast density (A) and remodeling tissue thickness(B) are displayed. Data is reported as average of 10 total viewing regions from biopsies of two separate pigs ± standard error. “X” indicates significant difference from Xeroform™ treated tissue, and “S” indicates significant difference from sIPN without drug treatment (P<0.05).
), and 21 (□) days. The 0.016 in dermatome cut depth wounds are shown on the left, whereas 0.022 in wounds are on the right. Fibroblast density (A) and remodeling tissue thickness(B) are displayed. Data is reported as average of 10 total viewing regions from biopsies of two separate pigs ± standard error. “X” indicates significant difference from Xeroform™ treated tissue, and “S” indicates significant difference from sIPN without drug treatment (P<0.05).Similar articles
-
Concurrent in vitro release of silver sulfadiazine and bupivacaine from semi-interpenetrating networks for wound management.J Burn Care Res. 2009 Jan-Feb;30(1):98-104. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3181921ed9. J Burn Care Res. 2009. PMID: 19060724 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional in situ photopolymerized semi-interpenetrating network system is an effective donor site dressing: a cross comparison study in a swine model.J Burn Care Res. 2009 Jan-Feb;30(1):37-45. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3181921f98. J Burn Care Res. 2009. PMID: 19131760 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of donor-site healing under Xeroform and Jelonet dressings: unexpected findings.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 Aug;112(2):430-9. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000070408.33700.C7. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. PMID: 12900600 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative study of Silver Sulfadiazine with other materials for healing and infection prevention in burns: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Burns. 2019 Mar;45(2):282-292. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Burns. 2019. PMID: 29903603
-
Silver sulfadiazine for the treatment of partial-thickness burns and venous stasis ulcers.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012 May;66(5):e159-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.06.014. Epub 2010 Aug 17. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 20724028 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomaterials modulate interleukin-8 and other inflammatory proteins during reepithelialization in cutaneous partial-thickness wounds in pigs.Wound Repair Regen. 2010 Sep-Oct;18(5):486-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2010.00609.x. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Wound Repair Regen. 2010. PMID: 20731797 Free PMC article.
-
Does antibiotic use accelerate or retard cutaneous repair? A systematic review in animal models.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 10;14(10):e0223511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223511. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31600279 Free PMC article.
-
Pain management via local anesthetics and responsive hydrogels.Ther Deliv. 2015 Feb;6(2):165-76. doi: 10.4155/tde.14.95. Ther Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25690085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of the addition of a labile gelatin component on the degradation and solute release kinetics of a stable PEG hydrogel.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012;23(12):1595-611. doi: 10.1163/092050611X587547. Epub 2012 May 11. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012. PMID: 21801489 Free PMC article.
-
Local delivery of allogeneic bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for cutaneous wound healing in a porcine model.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016 Feb;10(2):E90-E100. doi: 10.1002/term.1700. Epub 2013 Feb 18. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016. PMID: 23418160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brett DW. A review of moisture-control dressings in wound care. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2006 Nov-Dec;33(6 Suppl):S3–8. - PubMed
-
- Ayello EA. New evidence for an enduring wound-healing concept: moisture control. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2006 Nov-Dec;33(6 Suppl):S1–2. - PubMed
-
- Waldeck H, Chung AS, Kao WJ. Interpenetrating polymer networks containing gelatin modified with PEGylated RGD and soluble KGF: synthesis, characterization, and application in in vivo critical dermal wound. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007 Sep 15;82(4):861–871. - PubMed
-
- Phillips JM, Kao WJ. Macrophage adhesion on gelatin-based interpenetrating networks grafted with PEGylated RGD. Tissue Eng. 2005 May-Jun;11(5-6):964–973. - PubMed
-
- Witte RP, Blake AJ, Palmer C, Kao WJ. Analysis of poly(ethylene glycol)-diacrylate macromer polymerization within a multicomponent semi-interpenetrating polymer network system. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004 Dec 1;71(3):508–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

