Distinct requirements for achievement of allotolerance versus reversal of autoimmunity via nonmyeloablative mixed chimerism induction in NOD mice
- PMID: 20061915
- PMCID: PMC3043373
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181c4692e
Distinct requirements for achievement of allotolerance versus reversal of autoimmunity via nonmyeloablative mixed chimerism induction in NOD mice
Abstract
Objectives: Mixed hematopoietic chimerism is associated with islet allograft tolerance and may reverse autoimmunity. We developed low intensity regimens for the induction of mixed chimerism and examined the effects on autoimmunity in prediabetic nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice.
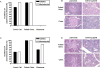
Research design and methods: NOD mice received various combinations of total body irradiation, anti-CD154, anti-CD8alpha, anti-CD4, and anti-Thy1.2 monoclonal antibodies, with or without transplantation of C57BL/6 bone marrow cells and were followed up for development of diabetes, chimerism, and donor skin graft survival. Autoimmunity was assessed by histologic examination of salivary glands and pancreata.
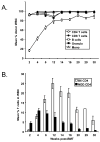
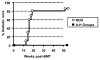
Results: Although conditioning alone prevented or delayed the onset of diabetes, stable mixed chimerism was required for the reversal of isletitis. Mixed chimerism and skin graft tolerance were achieved in NOD mice receiving anti-CD154 with bone marrow transplantation as the means of tolerizing peripheral CD4 T cells to alloantigens. However, isletitis was not reversed in allotolerant mixed chimeras prepared with this regimen.
Conclusions: Partial depletion of peripheral autoreactive NOD CD4 T cells is needed to achieve full reversal of isletitis by mixed chimerism induction from a protective donor strain, but it is not required for induction of specific tolerance to donor alloantigens. Thus, the requirements for tolerizing alloreactive and autoreactive NOD CD4 cells are distinct.
Figures
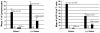


References
-
- Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM, Lakey JR, Shapiro AM. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2005;54:2060–2069. - PubMed
-
- Sykes M, Nikolic B. Treatment of severe autoimmune disease by stem-cell transplantation. Nature. 2005;435:620–627. - PubMed
-
- Nikolic B, Takeuchi Y, Leykin I, Fudaba Y, Smith RN, Sykes M. Mixed hematopoietic chimerism allows cure of autoimmune diabetes through allogeneic tolerance and reversal of autoimmunity. Diabetes. 2004;53:376–383. - PubMed
-
- Saliba RM, de Lima M, Giralt S, Andersson B, Khouri IF, Hosing C, Ghosh S, Neumann J, Hsu Y, De Jesus J, Qazilbash MH, Champlin RE, Couriel DR. Hyper-acute GVHD: risk factors, outcomes, and clinical implications. Blood. 2007;109:2751–2758. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

