APOBEC3 proteins mediate the clearance of foreign DNA from human cells
- PMID: 20062055
- PMCID: PMC2921484
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1744
APOBEC3 proteins mediate the clearance of foreign DNA from human cells
Abstract
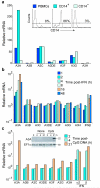
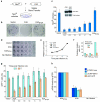
Bacteria evolved restriction endonucleases to prevent interspecies DNA transmission and bacteriophage infection. Here we show that human cells possess an analogous mechanism. APOBEC3A is induced by interferon following DNA detection, and it deaminates foreign double-stranded DNA cytidines to uridines. These atypical DNA nucleosides are converted by the uracil DNA glycosylase UNG2 to abasic lesions, which lead to foreign DNA degradation. This mechanism is evident in cell lines and primary monocytes, where up to 97% of cytidines in foreign DNA are deaminated. In contrast, cellular genomic DNA appears unaffected. Several other APOBEC3s also restrict foreign gene transfer. Related proteins exist in all vertebrates, indicating that foreign DNA restriction may be a conserved innate immune defense mechanism. The efficiency and fidelity of genetic engineering, gene therapy, and DNA vaccination are likely to be influenced by this anti-DNA defense system.
Figures


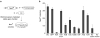
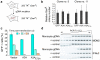
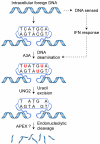
Comment in
-
Human cells clear foreign DNA.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Mar;11(3):172. doi: 10.1038/nrg2757. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 21485432 No abstract available.
References
Additional References for Online Methods
-
- Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res. 1998;8:175–185. - PubMed
References
-
- Medzhitov R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature. 2007;449:819–826. - PubMed
-
- Uematsu S, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and Type I interferons. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:15319–15323. - PubMed
-
- Takaoka A, et al. DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and an activator of innate immune response. Nature. 2007;448:501–505. - PubMed
-
- Roberts TL, et al. HIN-200 proteins regulate caspase activation in response to foreign cytoplasmic DNA. Science. 2009;323:1057–1060. - PubMed
-
- Burckstummer T, et al. An orthogonal proteomic-genomic screen identifies AIM2 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor for the inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:266–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

