Allosteric regulation of Argonaute proteins by miRNAs
- PMID: 20062058
- PMCID: PMC2834277
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1736
Allosteric regulation of Argonaute proteins by miRNAs
Abstract
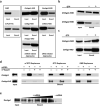
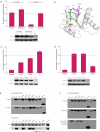
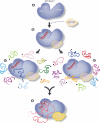
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) bind to Argonaute (AGO) family proteins to form a related set of effector complexes that have diverse roles in post-transcriptional gene regulation throughout the eukaryotic lineage. Here sequence and structural analysis of the MID domain of the AGO proteins identified similarities with a family of allosterically regulated bacterial ligand-binding domains. We used in vitro and in vivo approaches to show that certain AGO proteins (those involved in translational repression) have conserved this functional allostery between two distinct sites, one involved in binding miRNA-target duplex and the other in binding the 5' cap feature (m(7)GpppG) of eukaryotic mRNAs. This allostery provides an explanation for how miRNA-bound effector complexes may avoid indiscriminate repressive action (mediated through binding interactions with the cap) before full target recognition.
Figures


References
-
- Wu L, Belasco JG. Let me count the ways: mechanisms of gene regulation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol Cell. 2008;29:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Kiriakidou M, et al. An mRNA m(7)G cap binding-like motif within human Ago2 represses translation. Cell. 2007;129:1141–1151. - PubMed
-
- Pillai RS, et al. Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 MicroRNA in human cells. Science. 2005;309:1573–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

