Lipoid pneumonia presenting as non resolving community acquired pneumonia: a case report
- PMID: 20062592
- PMCID: PMC2803992
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-2-9332
Lipoid pneumonia presenting as non resolving community acquired pneumonia: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Lipoid pneumonia is a rare form of pneumonia caused by inhalation or aspiration of fat containing substances like, petroleum jelly, mineral oils, few laxatives etc. It usually presents as insidious onset chronic respiratory illness simulating interstitial lung diseases. Rarely, it may present as an acute respiratory illness, specially, when exposure to fatty substance is acute and/or massive. Radiologically, it may mimic carcinoma, acute or chronic pneumonia, ARDS, or a localized granuloma. Diagnosis of LP requires demonstration of lipid laden macrophages in sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid or fine needle aspiration cytology/biopsy from lung lesion. Treatment of this illness is poorly defined and constitutes supportive therapy and corticosteroids.
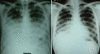
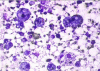
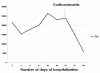
Case presentation: A 20-year old Indian farmer was referred to us with a diagnosis of non resolving community acquired pneumonia. Respiratory examination revealed signs of consolidation. Chest radiograph revealed findings suggestive of bilateral consolidation. Sputum and blood culture were sterile. He was treated with prolonged course of various antibiotics without any significant response. For evaluation of non resolving pneumonia fibreoptic bronchoscopy was done. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and biopsy from lung lesion showed lipid laden macrophages. Hence diagnosis of lipoid pneumonia was made. Patient was treated with course of corticosteroids with good response. Literature on this rare entity is discussed.
Conclusion: Lipoid pneumonia is a rare form of pneumonia which rarely present acutely resembling community acquired pneumonia and requires high degree of suspicion for diagnosis. Its treatment is difficult and poorly defined. However, prolonged corticosteroids may be effective.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipoid pneumonia: an uncommon entity.Indian J Med Sci. 2009 Oct;63(10):474-80. Indian J Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19901490 Review.
-
[Exogenous lipid pneumonia with hyperpyrexia: a case report].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Oct 18;50(5):921-923. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30337759 Chinese.
-
Lipoid pneumonia: an overview.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010 Dec;4(6):799-807. doi: 10.1586/ers.10.74. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010. PMID: 21128754 Review.
-
Exogenous lipoid pneumonia - a case report of a fire-eater.Pol J Radiol. 2012 Oct;77(4):60-4. doi: 10.12659/pjr.883631. Pol J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 23269939 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoid pneumonia: a silent complication of mineral oil aspiration.Pediatrics. 1999 Feb;103(2):E19. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.2.e19. Pediatrics. 1999. PMID: 9925865
Cited by
-
Endogenous lipoid pneumonia presenting as solitary pulmonary nodule: a case report.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9727-30. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464746 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia in normal and immunocompromised children: an overview and update.Radiol Clin North Am. 2011 Sep;49(5):895-920. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2011.06.007. Radiol Clin North Am. 2011. PMID: 21889014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult exogenous lipoid pneumonia: A rare and underrecognized entity in cytology - A case series.Cytojournal. 2018 Jul 13;15:17. doi: 10.4103/cytojournal.cytojournal_29_17. eCollection 2018. Cytojournal. 2018. PMID: 30112015 Free PMC article.
-
"Diesel siphoner's lung": Exogenous lipoid pneumonia following hydrocarbon aspiration.Lung India. 2014 Jan;31(1):63-6. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.125986. Lung India. 2014. PMID: 24669087 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Post-Primary Tuberculosis Which Was Pathologically Diagnosed as Lipoid Pneumonia.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Aug 4;15:4235-4239. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S367312. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35959148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams FD, Pittman H. Lipid pneumonia of right middle lobe. N Engl J Med. 1949;241(15):579–582. - PubMed
-
- Aibar Arregui MA, Laborda Ezquerra K, Conget Lopez F. Lipoid pneumonia related to an accidental aspiration of gas-oil. An Med Interna. 2007;24(4):187–189. - PubMed
-
- Levade T, Salvayre R, Dongay G, Dang QQ, Vieu C, Bessac A, Douste-Blazy L. Chemical analysis of the bronchoalveolar washing fluid in the diagnosis of liquid paraffin pneumonia. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1987;25(1):45–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

