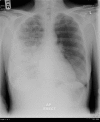
Severe Legionnaires disease complicated by multi-organ dysfunction in a previously healthy patient: a case report
- PMID: 20062668
- PMCID: PMC2803948
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-2-9151
Severe Legionnaires disease complicated by multi-organ dysfunction in a previously healthy patient: a case report
Abstract
A case of a previously healthy lady with community-acquired pneumonia who progressed to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute renal failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation and sepsis is reported. Treatment with antibiotics and various modes of mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit were successful. A urinary legionella antigen test was positive for Legionella pneumophila.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome from community-acquired legionella pneumonia: case report.Am J Crit Care. 2007 May;16(3):320, 317. Am J Crit Care. 2007. PMID: 17460326
-
[Early manifestation of septic shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation complicated by acute myocardial infarction in a patient suspected of having Legionnaires' disease].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1998 Mar;72(3):286-92. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.72.286. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9585703 Japanese.
-
Severe Legionella pneumophila pneumonia and non-invasive ventilation: presentation of two cases and brief review of the literature.Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2013;81(4):399-403. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2013. PMID: 23744171 Review.
-
[Community acquired pneumonia. Report of 8 cases of severe pneumonia by serogroup 1 Legionella pneumophila in Chile].Rev Med Chil. 2002 Mar;130(3):309-13. Rev Med Chil. 2002. PMID: 12043374 Spanish.
-
[Community-acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. Study of 97 cases].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2003 Oct;21(8):394-400. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2003. PMID: 14525703 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
A Prolonged Neurological Presentation of Legionnaire's Disease.Cureus. 2021 Jun 15;13(6):e15672. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15672. eCollection 2021 Jun. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34277263 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1beta expressing neutrophil extracellular traps in Legionella pneumophila infection.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1573151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1573151. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40547021 Free PMC article.
-
Rash, disseminated intravascular coagulation and legionella: Episode 10 and a rewind into the past.Respir Med Case Rep. 2015 May 8;15:95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2015.04.001. eCollection 2015. Respir Med Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26236615 Free PMC article.
-
Legionnaire's Disease Presenting With the Legionella Triad (Pneumonia, Rhabdomyolysis, and Renal Failure) and Cardiac Complications.Cureus. 2022 Jun 18;14(6):e26056. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26056. eCollection 2022 Jun. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35865426 Free PMC article.
-
Legionnaires Disease Presenting as Diarrhea: A Case Report.Cureus. 2020 Sep 22;12(9):e10593. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10593. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33110729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Bartlett JG, Campbell GD, Dean NC, Dowell SF, File TM Jr, Musher DM, Niederman MS, Torres A, Whitney CG. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:S27–72. doi: 10.1086/511159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources