Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan core beta-galactoside confers sensitivity towards nematotoxic fungal galectin CGL2
- PMID: 20062796
- PMCID: PMC2798750
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000717
Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan core beta-galactoside confers sensitivity towards nematotoxic fungal galectin CGL2
Abstract
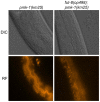
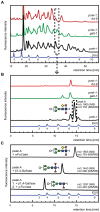
The physiological role of fungal galectins has remained elusive. Here, we show that feeding of a mushroom galectin, Coprinopsis cinerea CGL2, to Caenorhabditis elegans inhibited development and reproduction and ultimately resulted in killing of this nematode. The lack of toxicity of a carbohydrate-binding defective CGL2 variant and the resistance of a C. elegans mutant defective in GDP-fucose biosynthesis suggested that CGL2-mediated nematotoxicity depends on the interaction between the galectin and a fucose-containing glycoconjugate. A screen for CGL2-resistant worm mutants identified this glycoconjugate as a Galbeta1,4Fucalpha1,6 modification of C. elegans N-glycan cores. Analysis of N-glycan structures in wild type and CGL2-resistant nematodes confirmed this finding and allowed the identification of a novel putative glycosyltransferase required for the biosynthesis of this glycoepitope. The X-ray crystal structure of a complex between CGL2 and the Galbeta1,4Fucalpha1,6GlcNAc trisaccharide at 1.5 A resolution revealed the biophysical basis for this interaction. Our results suggest that fungal galectins play a role in the defense of fungi against predators by binding to specific glycoconjugates of these organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

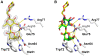
Similar articles
-
Galactosylated fucose epitopes in nematodes: increased expression in a Caenorhabditis mutant associated with altered lectin sensitivity and occurrence in parasitic species.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28276-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.353128. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22733825 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of the β-trefoil protein fold in the recognition and control of invertebrate predators and parasites by a fungal defence system.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(5):e1002706. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002706. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22615566 Free PMC article.
-
Galactoseβ1-4fucose: A unique disaccharide unit found in N-glycans of invertebrates including nematodes.Proteomics. 2016 Dec;16(24):3137-3147. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201600001. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27091793 Review.
-
Structure and functional analysis of the fungal galectin CGL2.Structure. 2004 Apr;12(4):689-702. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.03.002. Structure. 2004. PMID: 15062091
-
Strength in numbers: "Omics" studies of C. elegans innate immunity.Virulence. 2012 Oct 1;3(6):477-84. doi: 10.4161/viru.21906. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Virulence. 2012. PMID: 23076279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The secreted antifungal protein thionin 2.4 in Arabidopsis thaliana suppresses the toxicity of a fungal fruit body lectin from Fusarium graminearum.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(8):e1003581. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003581. Epub 2013 Aug 22. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23990790 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan shotgun array.Glycobiology. 2018 Apr 1;28(4):223-232. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwy002. Glycobiology. 2018. PMID: 29325093 Free PMC article.
-
Galactosylated fucose epitopes in nematodes: increased expression in a Caenorhabditis mutant associated with altered lectin sensitivity and occurrence in parasitic species.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28276-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.353128. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22733825 Free PMC article.
-
The class I α1,2-mannosidases of Caenorhabditis elegans.Glycoconj J. 2012 May;29(4):173-9. doi: 10.1007/s10719-012-9378-1. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Glycoconj J. 2012. PMID: 22535467
-
In vitro evaluation of the effect of galectins on Schistosoma mansoni motility.BMC Res Notes. 2023 Oct 10;16(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06530-9. BMC Res Notes. 2023. PMID: 37817269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loris R. Principles of structures of animal and plant lectins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1572:198–208. - PubMed
-
- Kohatsu L, Hsu DK, Jegalian AG, Liu FT, Baum LG. Galectin-3 induces death of Candida species expressing specific β1,2-linked mannans. J Immunol. 2006;177:4718–4726. - PubMed
-
- Griffitts JS, Haslam SM, Yang T, Garczynski SF, Mulloy B, et al. Glycolipids as receptors for Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin. Science. 2005;307:922–925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

