Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species
- PMID: 20062805
- PMCID: PMC2799520
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008613
Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species
Abstract
Background: The plant working group of the Consortium for the Barcode of Life recommended the two-locus combination of rbcL+matK as the plant barcode, yet the combination was shown to successfully discriminate among 907 samples from 550 species at the species level with a probability of 72%. The group admits that the two-locus barcode is far from perfect due to the low identification rate, and the search is not over.
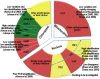
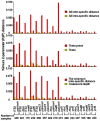
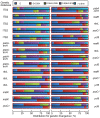
Methodology/principal findings: Here, we compared seven candidate DNA barcodes (psbA-trnH, matK, rbcL, rpoC1, ycf5, ITS2, and ITS) from medicinal plant species. Our ranking criteria included PCR amplification efficiency, differential intra- and inter-specific divergences, and the DNA barcoding gap. Our data suggest that the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS2) of nuclear ribosomal DNA represents the most suitable region for DNA barcoding applications. Furthermore, we tested the discrimination ability of ITS2 in more than 6600 plant samples belonging to 4800 species from 753 distinct genera and found that the rate of successful identification with the ITS2 was 92.7% at the species level.
Conclusions: The ITS2 region can be potentially used as a standard DNA barcode to identify medicinal plants and their closely related species. We also propose that ITS2 can serve as a novel universal barcode for the identification of a broader range of plant taxa.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of species in the angiosperm family Apiaceae using DNA barcodes.Mol Ecol Resour. 2014 Nov;14(6):1231-8. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12262. Epub 2014 May 14. Mol Ecol Resour. 2014. PMID: 24739357
-
DNA barcoding Chinese medicinal Bupleurum.Phytomedicine. 2014 Nov 15;21(13):1767-73. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Phytomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25444445
-
[DNA bacording of Verbenaceae medicinal plant by using ITS2 and psbA-trnH region].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;37(8):1107-13. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22779359 Chinese.
-
Applying plant DNA barcodes for Rosaceae species identification.Cladistics. 2011 Apr;27(2):165-170. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-0031.2010.00328.x. Cladistics. 2011. PMID: 34875771 Review.
-
A renaissance in herbal medicine identification: from morphology to DNA.Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Nov 15;32(7):1237-1244. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 25087935 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular identification of Aquilaria species with distribution records in China using DNA barcode technology.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Apr 26;6(4):1525-1535. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1914210. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 33969211 Free PMC article.
-
Endolithic Fungal Diversity in Antarctic Oligocene Rock Samples Explored Using DNA Metabarcoding.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;13(6):414. doi: 10.3390/biology13060414. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927294 Free PMC article.
-
Airborne DNA reveals predictable spatial and seasonal dynamics of fungi.Nature. 2024 Jul;631(8022):835-842. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07658-9. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38987593 Free PMC article.
-
Flowers in Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) Pollinator Plantings and the Upper Midwest Agricultural Landscape Supporting Honey Bees.Insects. 2020 Jun 30;11(7):405. doi: 10.3390/insects11070405. Insects. 2020. PMID: 32629811 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of DNA Barcoding on Recently Diverged Species in the Genus Gentiana (Gentianaceae) in China.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 6;11(4):e0153008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153008. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27050315 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

