Role of the amygdala in antidepressant effects on hippocampal cell proliferation and survival and on depression-like behavior in the rat
- PMID: 20062812
- PMCID: PMC2799663
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008618
Role of the amygdala in antidepressant effects on hippocampal cell proliferation and survival and on depression-like behavior in the rat
Abstract
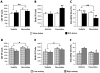
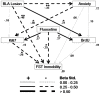
The stimulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by antidepressants has been associated with multiple molecular pathways, but the potential influence exerted by other brain areas has received much less attention. The basolateral complex of the amygdala (BLA), a region involved in anxiety and a site of action of antidepressants, has been implicated in both basal and stress-induced changes in neural plasticity in the dentate gyrus. We investigated here whether the BLA modulates the effects of the SSRI antidepressant fluoxetine on hippocampal cell proliferation and survival in relation to a behavioral index of depression-like behavior (forced swim test). We used a lesion approach targeting the BLA along with a chronic treatment with fluoxetine, and monitored basal anxiety levels given the important role of this behavioral trait in the progress of depression. Chronic fluoxetine treatment had a positive effect on hippocampal cell survival only when the BLA was lesioned. Anxiety was related to hippocampal cell survival in opposite ways in sham- and BLA-lesioned animals (i.e., negatively in sham- and positively in BLA-lesioned animals). Both BLA lesions and low anxiety were critical factors to enable a negative relationship between cell proliferation and depression-like behavior. Therefore, our study highlights a role for the amygdala on fluoxetine-stimulated cell survival and on the establishment of a link between cell proliferation and depression-like behavior. It also reveals an important modulatory role for anxiety on cell proliferation involving both BLA-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Our findings underscore the amygdala as a potential target to modulate antidepressants' action in hippocampal neurogenesis and in their link to depression-like behaviors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
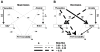
Similar articles
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is critically involved in basal and fluoxetine-stimulated adult hippocampal cell proliferation and in anxiety, depression, and memory-related behaviors.Mol Psychiatry. 2011 May;16(5):533-47. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.15. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Mol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 20177408
-
Depression and adult neurogenesis: Positive effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine and of physical exercise.Brain Res Bull. 2018 Oct;143:181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 30236533 Review.
-
Effects of fluoxetine on CRF and CRF1 expression in rats exposed to the learned helplessness paradigm.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Feb;225(3):647-59. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2859-x. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 22960774
-
Subchronic treatment with fluoxetine and ketanserin increases hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor, β-catenin and antidepressant-like effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4b):1046-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01516.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21627639 Free PMC article.
-
A review and update of mechanisms of estrogen in the hippocampus and amygdala for anxiety and depression behavior.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Jun;31(6):1097-111. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301067. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16554740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction Effect of Social Isolation and High Dose Corticosteroid on Neurogenesis and Emotional Behavior.Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Feb 21;11:18. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00018. eCollection 2017. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28270754 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis as a pharmacological strategy to improve behavioural deficits in a putative mouse model of post-traumatic stress disorder.J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Jan;24(1):102-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02234.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21981145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noradrenergic activation of the basolateral amygdala maintains hippocampus-dependent accuracy of remote memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 22;114(34):9176-9181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710819114. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28790188 Free PMC article.
-
Not all stress is equal: CREB is not necessary for restraint stress reinstatement of cocaine-conditioned reward.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Jun 1;246:63-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.02.026. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23458740 Free PMC article.
-
Using causal models to distinguish between neurogenesis-dependent and -independent effects on behaviour.J R Soc Interface. 2012 May 7;9(70):907-17. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2011.0510. Epub 2011 Sep 28. J R Soc Interface. 2012. PMID: 21957118 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

