Complement inhibition by gram-positive pathogens: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 20062962
- PMCID: PMC2832872
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-009-0572-y
Complement inhibition by gram-positive pathogens: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications
Abstract
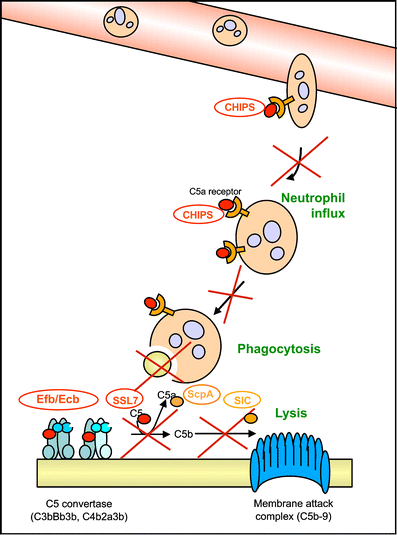
The plasma proteins of the complement system are essential in the innate immune response against bacteria. Complement labels bacteria with opsonins to support phagocytosis and generates chemoattractants to attract phagocytes to the site of infection. In turn, bacterial human pathogens have evolved different strategies to specifically impair the complement response. Here, we review the large arsenal of complement inhibitors produced by the gram-positive pathogens Staphylococcus aureus and Group A Streptococcus. We discuss how these bacterial molecules provide us with new tools to treat both infectious and inflammatory disease conditions in humans.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Understanding how leading bacterial pathogens subvert innate immunity to reveal novel therapeutic targets.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 Jul;120(1):13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.06.005. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17606031 Review.
-
Catch Me if You Can: Streptococcus pyogenes Complement Evasion Strategies.J Innate Immun. 2019;11(1):3-12. doi: 10.1159/000492944. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Innate Immun. 2019. PMID: 30269134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus versus Streptococcus pyogenes in hand infection.Infect Dis (Lond). 2015;47(10):747-8. doi: 10.3109/23744235.2015.1049463. Epub 2015 May 20. Infect Dis (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25990679 No abstract available.
-
[Toxic shock syndrome].Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2015 Oct;64(4):210-20. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2015. PMID: 26795225 Review. Czech.
-
Interaction of gram-positive microorganisms with complement.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;121:159-87. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45604-6_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985. PMID: 3936681 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Complement Evasion Strategies of Human Pathogenic Bacteria.Indian J Microbiol. 2020 Sep;60(3):283-296. doi: 10.1007/s12088-020-00872-9. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Indian J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32655196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposed drugs block toxin-driven platelet clearance by the hepatic Ashwell-Morell receptor to clear Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia.Sci Transl Med. 2021 Mar 24;13(586):eabd6737. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd6737. Sci Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33762439 Free PMC article.
-
A Mathematical Model of the Dynamics of Cytokine Expression and Human Immune Cell Activation in Response to the Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 10;11:711153. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.711153. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34869049 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus proteins Sbi and Efb recruit human plasmin to degrade complement C3 and C3b.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047638. Epub 2012 Oct 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071827 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Response Modulation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Persister Cells.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0005623. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00056-23. Epub 2023 Mar 15. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36920189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartmann K, Henz BM, Krüger-Krasagakes S, Köhl J, Burger R, Guhl S, Haase I, Lippert U, Zuberbier T. C3a and C5a stimulate chemotaxis of human mast cells. Blood. 1997;89:2863–2870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

