The effect of an intramedullary implant with a static magnetic field on the healing of the osteotomised rabbit femur
- PMID: 20062989
- PMCID: PMC3014488
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-009-0932-9
The effect of an intramedullary implant with a static magnetic field on the healing of the osteotomised rabbit femur
Abstract
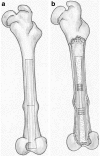
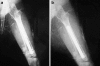
Static magnetic fields are a type of electromagnetic fields used in clinical practice. To ascertain what effect a static magnetic intramedullary device implanted in the rabbit femur had on fracture healing, 20 male New Zealand white rabbits with magnetic/nonmagnetic intramedullary implants were examined histologically, radiologically and for bone mineral density. Three groups were constituted according to the poles of the magnets. During surgery the intramedullary device was driven into the medulla. A femoral osteotomy was created with a mini Gigli wire at the centre point of the rod. Radiographs were obtained at the second and fourth weeks. Histological examination and bone mineral density were evaluated at the fourth week. The results of this study verified that an intramedullary implant with a static magnetic field improves bone healing in the first two weeks radiologically and that the configuration difference in magnetic poles has an effect on bone quality. Static magnetic fields have minor effects on bone mineral density values.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of nail rigidity on fracture healing. Strength and mineralisation in rat femoral bone.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998;118(1-2):7-13. doi: 10.1007/s004020050301. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998. PMID: 9833097
-
Comparison of non-compression and compression interlocking intramedullary nailing in rabbit femoral shaft osteotomy model.Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017 Apr;28(1):7-12. doi: 10.5606/ehc.2017.54333. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017. PMID: 28291432
-
Graded exchange reaming and nailing of non-unions. Strength and mineralisation in rat femoral bone.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998;118(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s004020050300. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998. PMID: 9833096
-
Impact of Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of Femur Fractures An Evolutionary Perspective.Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2018 Mar;76(1):9-13. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2018. PMID: 29537951 Review.
-
Treatment strategies for proximal femur fractures in osteoporotic patients.Osteoporos Int. 2005 Mar;16 Suppl 2:S93-S102. doi: 10.1007/s00198-004-1746-7. Epub 2004 Oct 16. Osteoporos Int. 2005. PMID: 15502962 Review.
Cited by
-
Signalling pathways underlying pulsed electromagnetic fields in bone repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 24;12:1333566. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1333566. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38328443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moderate static magnetic field promotes fracture healing and regulates iron metabolism in mice.Biomed Eng Online. 2023 Nov 15;22(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12938-023-01170-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2023. PMID: 37968671 Free PMC article.
-
Physical stimulations and their osteogenesis-inducing mechanisms.Int J Bioprint. 2018 Jun 11;4(2):138. doi: 10.18063/IJB.v4i2.138. eCollection 2018. Int J Bioprint. 2018. PMID: 33102916 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate SMFs attenuate bone loss in mice by promoting directional osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Nov 16;11(1):487. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02004-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33198804 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Exposure to Static Magnetic Fields from Magnetic Resonance Imaging Devices Deserves Screening for Osteoporosis and Vitamin D Levels: A Rat Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Jul 30;12(8):8919-32. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120808919. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26264009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basset CAL, Mitchell SN, Gaston SR. Treatment of ununited tibial diaphyseal fractures with pulsing electromagnetic fields. J Bone Joint Surg. 1981;63:511–523. - PubMed
-
- Basset CAL, Mitchell SN, Hernandez E. Modification of fracture repair with selected pulsing electromagnetic fields. J Bone Joint Surg. 1982;64(A):888–895. - PubMed
-
- Bassett CAL. Beneficial effects of electromagnetic fields. J Cell Biochem. 1993;51:387–393. - PubMed
-
- Brighton CT, Friedenberg ZB, Mitchell EI, Booth RE. Treatment of nonunion with constant direct current. Clin Orthop. 1977;124:106–123. - PubMed
-
- Brighton CT, Solomon R, Pollack SR. Treatment of recalcitrant non-union with a capacitatively coupled electrical field. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67:577–585. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

