Ruthenium nitrosyls derived from tetradentate ligands containing carboxamido-N and phenolato-o donors: syntheses, structures, photolability, and time dependent density functional theory studies
- PMID: 20063858
- PMCID: PMC2838436
- DOI: 10.1021/ic9017129
Ruthenium nitrosyls derived from tetradentate ligands containing carboxamido-N and phenolato-o donors: syntheses, structures, photolability, and time dependent density functional theory studies
Abstract
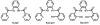
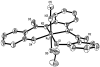
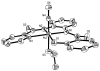
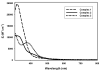
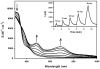
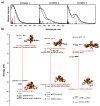
In order to examine the role(s) of designed ligands on the NO photolability of {Ru-NO}(6) nitrosyls, a set of three nitrosyls with ligands containing two carboxamide groups along with a varying number of phenolates have been synthesized. The nitrosyls namely, (NEt(4))(2)[(hybeb)Ru(NO)(OEt)] (1), (PPh(4))[(hypyb)Ru(NO)(OEt)] (2), and [(bpb)Ru(NO)(OEt)] (3) have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Complexes 1-3 are diamagnetic, exhibit nu(NO) in the range 1780-1840 cm(-1) and rapidly release NO in solution upon exposure to low power UV light (7 mW/cm(2)). Density Functional Theory (DFT) and Time Dependent DFT (TDDFT) calculations on 1-3 indicate considerable contribution of ligand orbitals in the MOs involved in transitions leading to NO photolability. The results of the theoretical studies match well with the experimental absorption spectra as well as the parameters for NO photorelease and provide insight into the transition(s) associated with loss of NO.
Figures
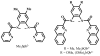
Similar articles
-
Dye-tethered ruthenium nitrosyls containing planar dicarboxamide tetradentate N4 ligands: effects of in-plane ligand twist on NO photolability.Inorg Chem. 2011 Jan 3;50(1):317-24. doi: 10.1021/ic1019873. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21114262
-
Accelerated photorelease of NO from {Ru-NO}6 nitrosyls containing carboxamido-N and carboxylato-O donors: syntheses, structures, and photochemistry.Inorg Chem. 2009 Feb 16;48(4):1490-7. doi: 10.1021/ic801748t. Inorg Chem. 2009. PMID: 20560617
-
Ruthenium nitrosyls derived from polypyridine ligands with carboxamide or imine nitrogen donor(s): isoelectronic complexes with different NO photolability.Inorg Chem. 2007 Mar 19;46(6):2328-38. doi: 10.1021/ic0620945. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Inorg Chem. 2007. PMID: 17315866
-
Triggered dye release via photodissociation of nitric oxide from designed ruthenium nitrosyls: turn-ON fluorescence signaling of nitric oxide delivery.Inorg Chem. 2011 Sep 19;50(18):9045-52. doi: 10.1021/ic201242d. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21815610
-
Photoactive ruthenium nitrosyls as NO donors: how to sensitize them toward visible light.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Apr 19;44(4):289-98. doi: 10.1021/ar100155t. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21361269 Review.
Cited by
-
2,2'-Dihydroxy-N,N'-(ethane-1,2-di-yl)di-benzamide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013 Feb 1;69(Pt 2):o201. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812051963. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013. PMID: 23424485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ignarro LJ. Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology. Academic Press; San Diego: 2000.
-
- Kalsner S, editor. Nitric Oxide Free Radicals in Peripheral Neurotransmission. Birkhauser; Boston: 2000.
-
- Fukuto JM, Wink DA. Met Ions Biol Syst. 1999;36:547–595. - PubMed
-
- Ko GY, Fang FC. Nitric Oxide and Infection. Kluwer Academic/ Plenum Publishers; New York: 1999.
-
- Lincoln J, Burnstock G. Nitric Oxide in Health and Disease. Cambridge University Press; New York: 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

