A motivational theory of life-span development
- PMID: 20063963
- PMCID: PMC2820305
- DOI: 10.1037/a0017668
A motivational theory of life-span development
Abstract
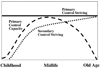
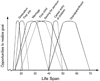
This article had four goals. First, the authors identified a set of general challenges and questions that a life-span theory of development should address. Second, they presented a comprehensive account of their Motivational Theory of Life-Span Development. They integrated the model of optimization in primary and secondary control and the action-phase model of developmental regulation with their original life-span theory of control to present a comprehensive theory of development. Third, they reviewed the relevant empirical literature testing key propositions of the Motivational Theory of Life-Span Development. Finally, because the conceptual reach of their theory goes far beyond the current empirical base, they pointed out areas that deserve further and more focused empirical inquiry.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Agency and Motivation in Adulthood and Old Age.Annu Rev Psychol. 2019 Jan 4;70:191-217. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010418-103043. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Annu Rev Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30110574 Review.
-
The control processes and subjective well-being of Chinese teachers: evidence of convergence with and divergence from the key propositions of the motivational theory of life-span development.Front Psychol. 2014 May 21;5:467. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00467. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 24904483 Free PMC article.
-
The primacy of primary control is a human universal: a reply to Gould's (1999) critique of the life-span theory of control.Psychol Rev. 1999 Jul;106(3):605-9. doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.106.3.605. Psychol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10467898 Review.
-
Motivational Congruence Theory: Beyond the Dualistic Approach to Human Motivation.Integr Psychol Behav Sci. 2024 Dec;58(4):1668-1683. doi: 10.1007/s12124-023-09793-w. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Integr Psychol Behav Sci. 2024. PMID: 37460900
-
Motivational beliefs, values, and goals.Annu Rev Psychol. 2002;53:109-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135153. Annu Rev Psychol. 2002. PMID: 11752481 Review.
Cited by
-
Daily goal progress is facilitated by spousal support and promotes psychological, physical, and relational well-being throughout adulthood.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2016 Sep;111(3):317-40. doi: 10.1037/pspi0000062. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27560610 Free PMC article.
-
Brooding Is Related to Neural Alterations during Autobiographical Memory Retrieval in Aging.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Sep 16;8:219. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00219. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27695414 Free PMC article.
-
Getting better with age: the relationship between age, acceptance, and negative affect.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2013 Apr;104(4):734-49. doi: 10.1037/a0031180. Epub 2012 Dec 31. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23276266 Free PMC article.
-
Encouraging Realistic Expectations in STEM Students: Paradoxical Effects of a Motivational Intervention.Front Psychol. 2016 Jul 26;7:1109. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01109. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27507955 Free PMC article.
-
Invited Commentary: Societal Constraints and Individual Agency: Navigating Educational Transitions for Upward Mobility.J Youth Adolesc. 2021 Mar;50(3):437-445. doi: 10.1007/s10964-020-01311-0. Epub 2020 Sep 5. J Youth Adolesc. 2021. PMID: 32892318
References
-
- Achtziger A, Gollwitzer PM. Motivation and volition in the course of action. In: Heckhausen J, Heckhausen H, editors. Motivation and action. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2008. pp. 272–295.
-
- Ashman O, Shiomura K, Levy BR. Influence of culture and age on control beliefs: The missing link of interdependence. International Journal of Aging and Human Development. 2006;62:143–157. - PubMed
-
- Aspinwall LG, Richter L. Optimism and self-mastery predict more rapid disengagement from unsolvable tasks in the presence of alternatives. Motivation and Emotion. 1999;23:221–245.
-
- Azuma H. Secondary control as a heterogeneous category. American Psychologist. 1984;39:970–971.
-
- Babb KA, Levine LJ, Arseneault JM. Shifting gears: Coping flexibility in children with and without ADHD. International Journal of Behavioral Development. (in press)

