Allostasis and the human brain: Integrating models of stress from the social and life sciences
- PMID: 20063966
- PMCID: PMC2808193
- DOI: 10.1037/a0017773
Allostasis and the human brain: Integrating models of stress from the social and life sciences
Abstract
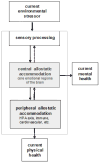
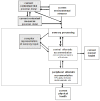
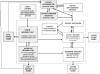
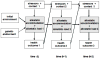
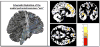
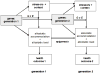
We draw on the theory of allostasis to develop an integrative model of the current stress process that highlights the brain as a dynamically adapting interface between the changing environment and the biological self. We review evidence that the core emotional regions of the brain constitute the primary mediator of the well-established association between stress and health, as well as the neural focus of wear and tear due to ongoing adaptation. This mediation, in turn, allows us to model the interplay over time between context, current stressor exposure, internal regulation of bodily processes, and health outcomes. We illustrate how this approach facilitates the integration of current findings in human neuroscience and genetics with key constructs from stress models from the social and life sciences, with implications for future research and the design of interventions targeting individuals at risk.
Figures
References
-
- Adamec RE, Blundell J, Burton P. Neural circuit changes mediating lasting brain and behavioral response to predator stress. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Review. 2005;29:1225–1241. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R. Is the human amygdala specialized for processing social information? New York Academy of Sciences. 2003;985:319–353. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D, Buchanan TW. Amygdala damage impairs emotional memory for gist but not details of complex stimuli. Nature Neuroscience. 2005;8:512–518. - PubMed
-
- Albert TJ, Dempesy CW, Sorenson CA. Anterior cerebellar vermal stimulation: effect on behavior and basal forebrain neurochemistry in rat. Biological Psychiatry. 1985;20:1267–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

