Role of nitric oxide signaling in endothelial differentiation of embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 20064011
- PMCID: PMC3121801
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2009.0417
Role of nitric oxide signaling in endothelial differentiation of embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Signaling pathways that govern embryonic stem cell (ESCs) differentiation are not well characterized. Nitric oxide (NO) is a potent vasodilator that modulates other signaling pathways in part by activating soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) to produce cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Because of its importance in endothelial cell (EC) growth in the adult, we hypothesized that NO may play a critical role in EC development. Accordingly, we assessed the role of NO in ESC differentiation into ECs. Murine ESCs differentiated in the presence of NO synthase (NOS) inhibitor NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME) for up to 11 days were not significantly different from vehicle-treated cells in EC markers. However, by 14 days, L-NAME-treated cells manifested modest reduction in EC markers CD144, FLK1, and endothelial NOS. ESC-derived ECs generated in the presence of L-NAME exhibited reduced tube-like formation in Matrigel. To understand the discrepancy between early and late effects of L-NAME, we assessed the NOS machinery and observed low mRNA expression of NOS and sGC subunits in ESCs, compared to differentiating cells after 14 days. In response to NO donors or activation of NOS or sGC, cellular cGMP levels were undetectable in undifferentiated ESCs, at low levels on day 7, and robustly increased in day 14 cells. Production of cGMP upon NOS activation at day 14 was inhibited by L-NAME, confirming endogenous NO dependence. Our data suggest that NOS elements are present in ESCs but inactive until later stages of differentiation, during which period NOS inhibition reduces expression of EC markers and impairs angiogenic function.
Figures

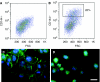

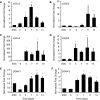


Similar articles
-
Role of nitric oxide signaling components in differentiation of embryonic stem cells into myocardial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 2;105(48):18924-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810230105. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19020077 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP are involved in angiotensin II AT(2) receptor effects on neurite outgrowth in NG108-15 cells.Neuroendocrinology. 2002 Jan;75(1):70-81. doi: 10.1159/000048222. Neuroendocrinology. 2002. PMID: 11810036
-
Icariin stimulates the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells via activating the PI3K-AKT-eNOS-NO-cGMP-PKG.Bone. 2014 Sep;66:189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.06.016. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Bone. 2014. PMID: 24956021
-
Formation, signaling functions, and metabolisms of nitrated cyclic nucleotide.Nitric Oxide. 2013 Nov 1;34:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Nitric Oxide. 2013. PMID: 23632125 Review.
-
Regulation and Pharmacology of the Cyclic GMP and Nitric Oxide Pathway in Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells.Cells. 2024 Dec 5;13(23):2008. doi: 10.3390/cells13232008. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial patterning of endothelium modulates cell morphology, adhesiveness and transcriptional signature.Biomaterials. 2013 Apr;34(12):2928-37. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.017. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23357369 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial Extracellular Matrix Microenvironments for Probing Endothelial Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 26;7(1):6551. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06986-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28747756 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of cellular glucose uptake by reactive species: a promising approach for diabetes therapy.RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 8;8(18):9887-9894. doi: 10.1039/c7ra13389h. eCollection 2018 Mar 5. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540836 Free PMC article.
-
Microfibrous Scaffolds Enhance Endothelial Differentiation and Organization of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2017 Oct;10(5):417-432. doi: 10.1007/s12195-017-0502-y. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2017. PMID: 28936269 Free PMC article.
-
Elastin-like protein hydrogels with controllable stress relaxation rate and stiffness modulate endothelial cell function.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023 Jul;111(7):896-909. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37520. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023. PMID: 36861665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomson JA. Itskovitz-Eldor J. Shapiro SS. Waknitz MA. Swiergiel JJ. Marshall VS. Jones JM. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Reubinoff BE. Pera MF. Fong CY. Trounson A. Bongso A. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: Somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Behfar A. Zingman LV. Hodgson DM. Rauzier JM. Kane GC. Terzic A. Pucéat M. Stem cell differentiation requires a paracrine pathway in the heart. FASEB J. 2002;16:1558–1566. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita J. Itoh H. Hirashima M. Ogawa M. Nishikawa S. Yurugi T. Naito M. Nakao K. Nishikawa S. Flk1-positive cells derived from embryonic stem cells serve as vascular progenitors. Nature. 2000;408:92–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

